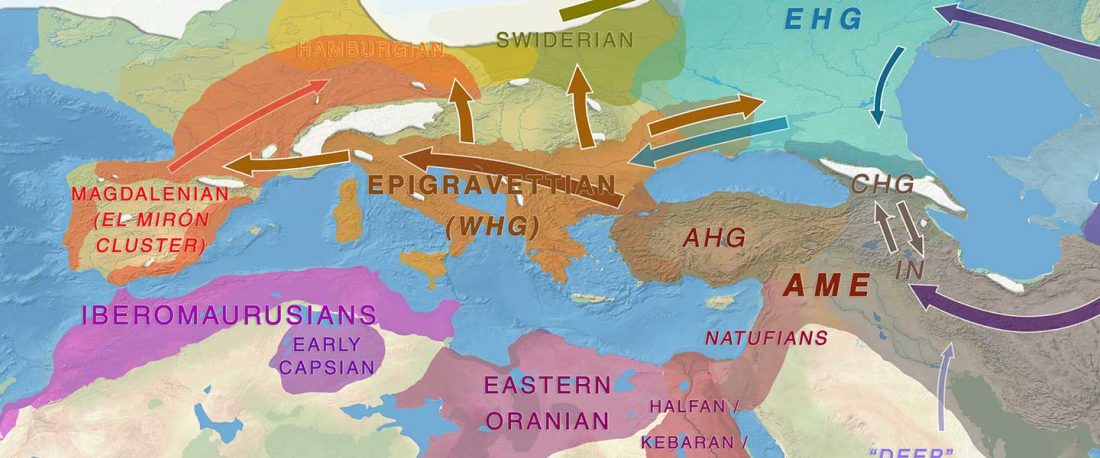
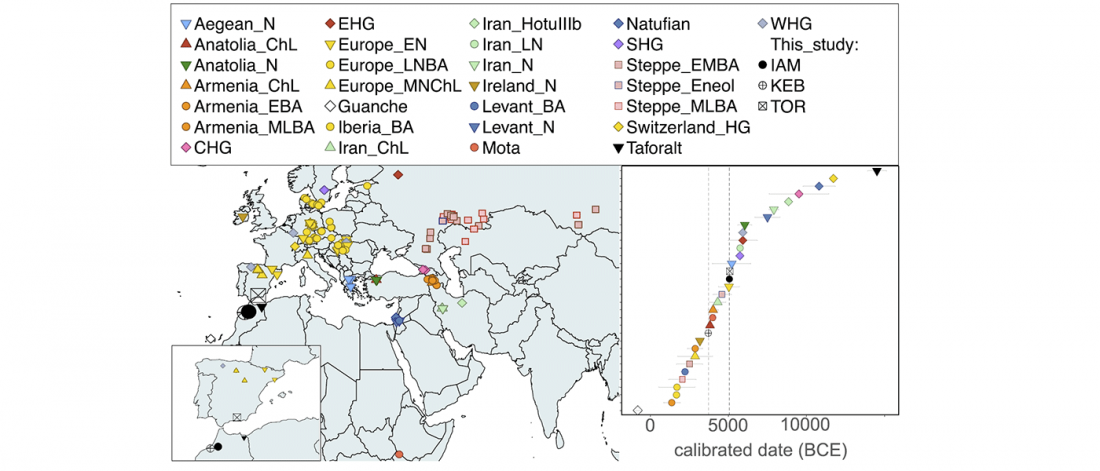
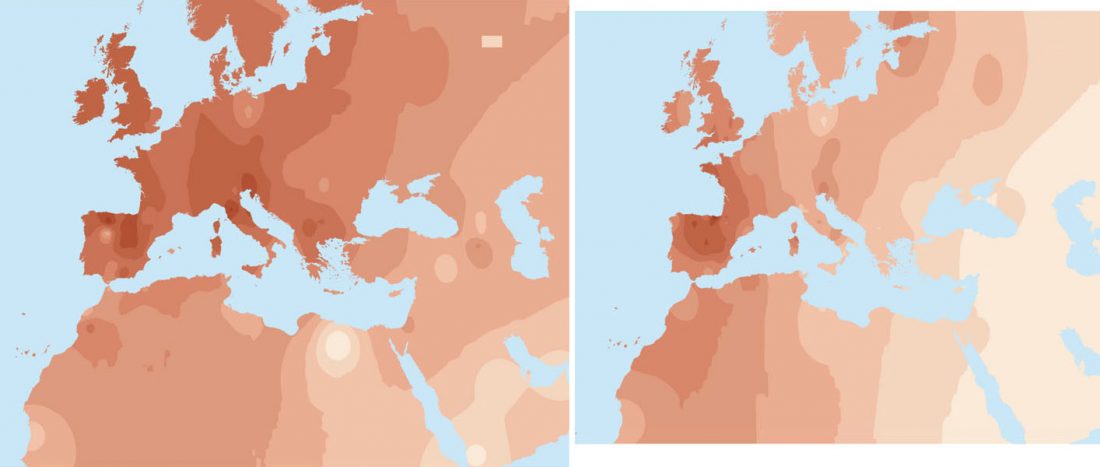
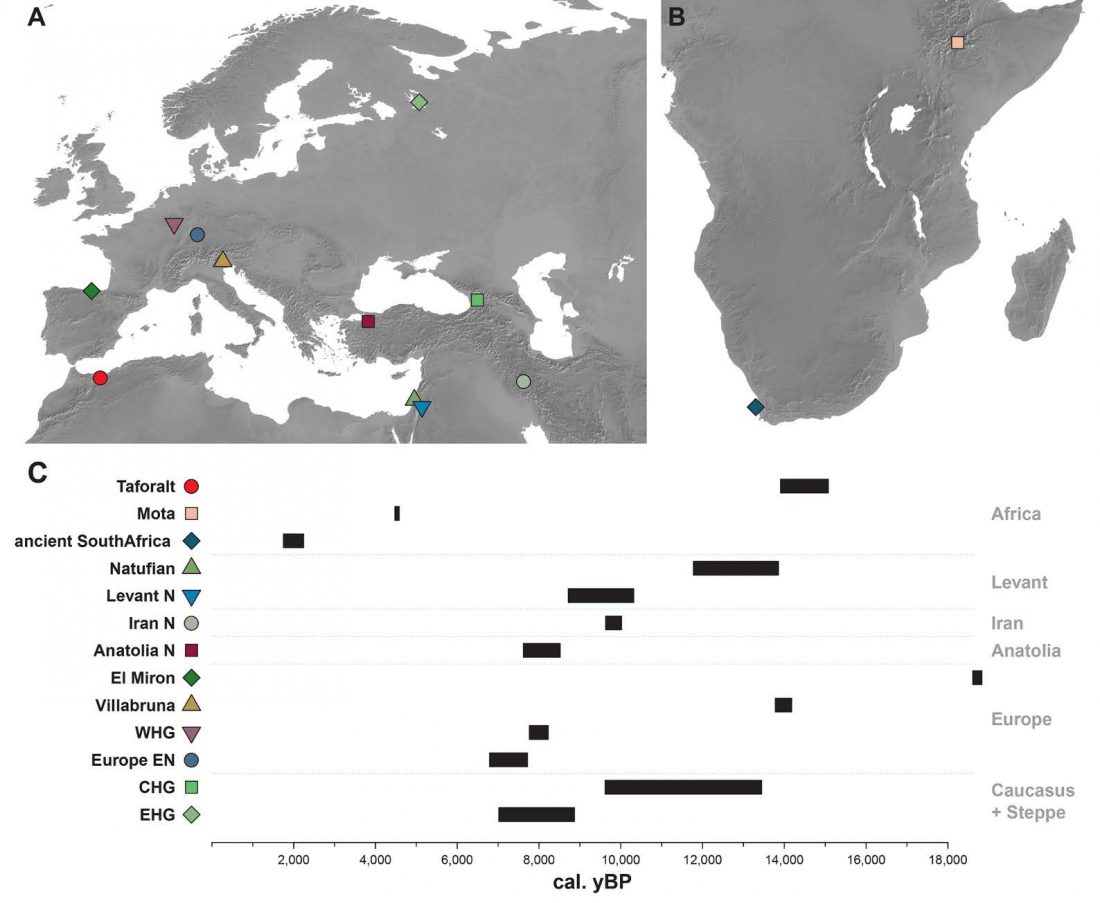
New preprint Late Upper Palaeolithic hunter-gatherers in the Central Mediterranean: new archaeological and genetic data from the Late Epigravettian burial Oriente C (Favignana, Sicily), by Catalano et al. bioRxiv (2019).
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
Grotta d’Oriente is a small coastal cave located on the island of Favignana, the largest (~20 km2) of a group of small islands forming the Egadi Archipelago, ~5 km from the NW coast of Sicily.
… Read the rest “Villabruna cluster in Late Epigravettian Sicily supports South Italian corridor for R1b-V88”The Oriente C funeral pit opens in the lower portion of layer 7, specifically sublayer 7D. Two radiocarbon dates on charcoal from the sublayers 7D (12149±65 uncal. BP) and 7E,