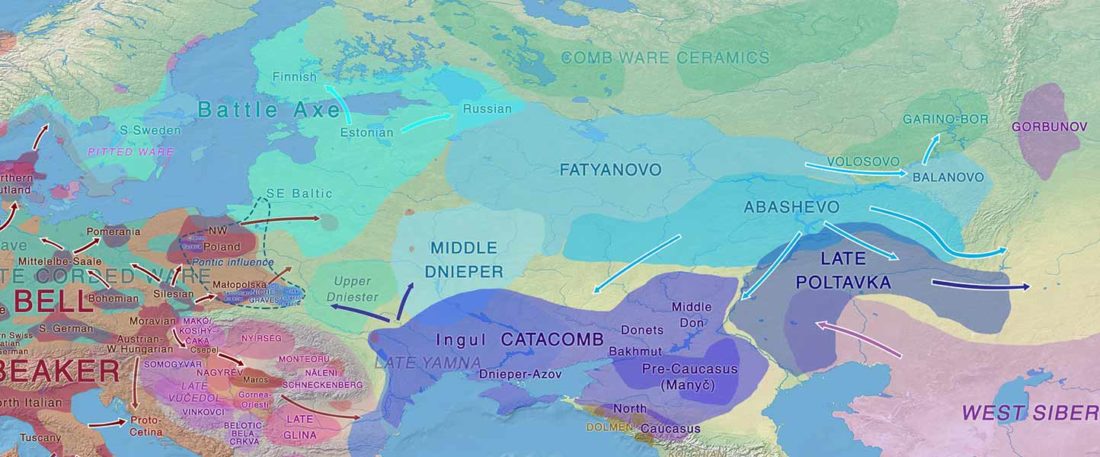
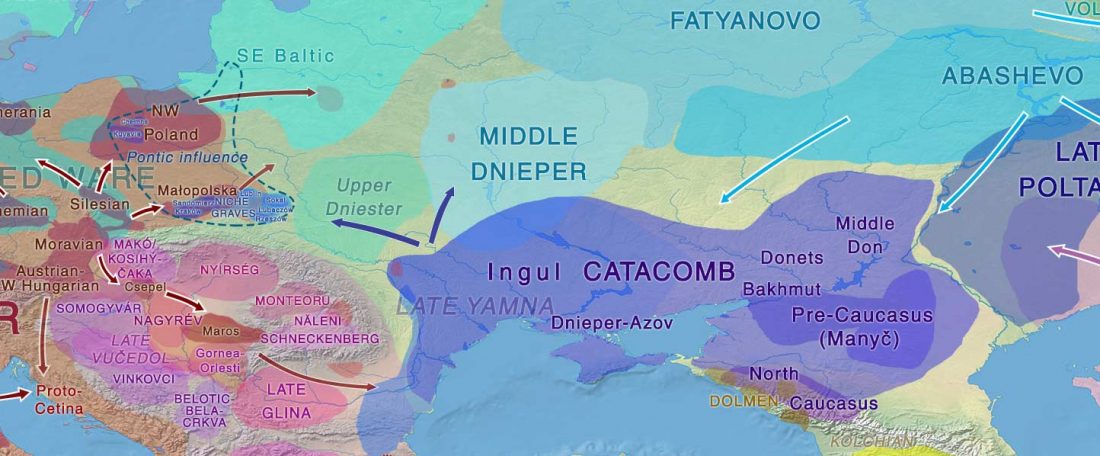
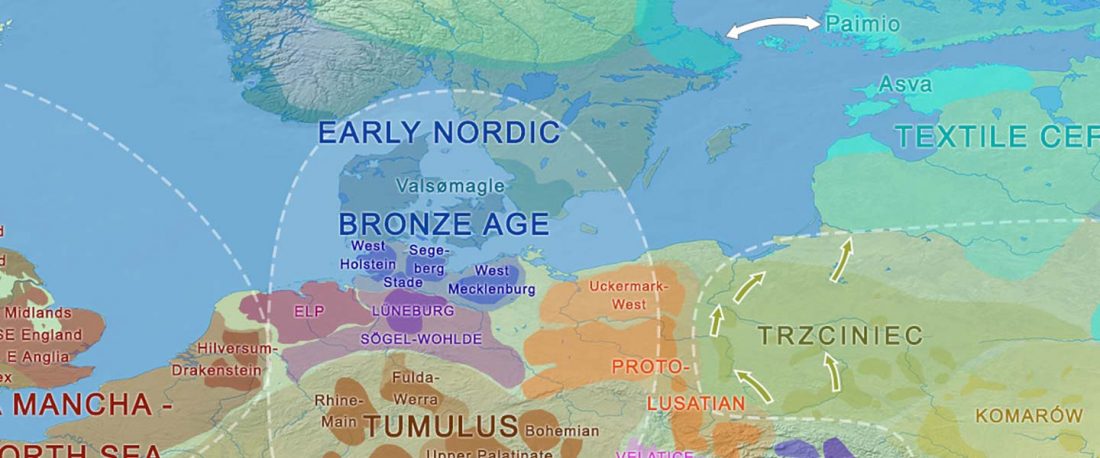
Open access Genetic ancestry changes in Stone to Bronze Age transition in the East European plain, by Saag et al. bioRxiv (2020).
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
Y-DNA chromosome haplogroup
… Read the rest “R1a-Z93-rich Classical CWC-like Fatyanovo replaced Volosovo”(…) the Bronze Age Fatyanovo Culture individuals [] maternal (subclades of mtDNA hg U5, U4, U2e, H, T, W, J, K, I and N1a) and paternal (chrY hg R1a-M417) lineages were ones characteristic of CWC individuals elsewhere in Europe. Interestingly, in all individuals for which the chrY hg could be determined with more depth (n=6), it was R1a2-Z93, a lineage now spread in Central and South Asia, rather than the