I have just uploaded a new working draft of the third version of the Indo-European demic diffusion model.
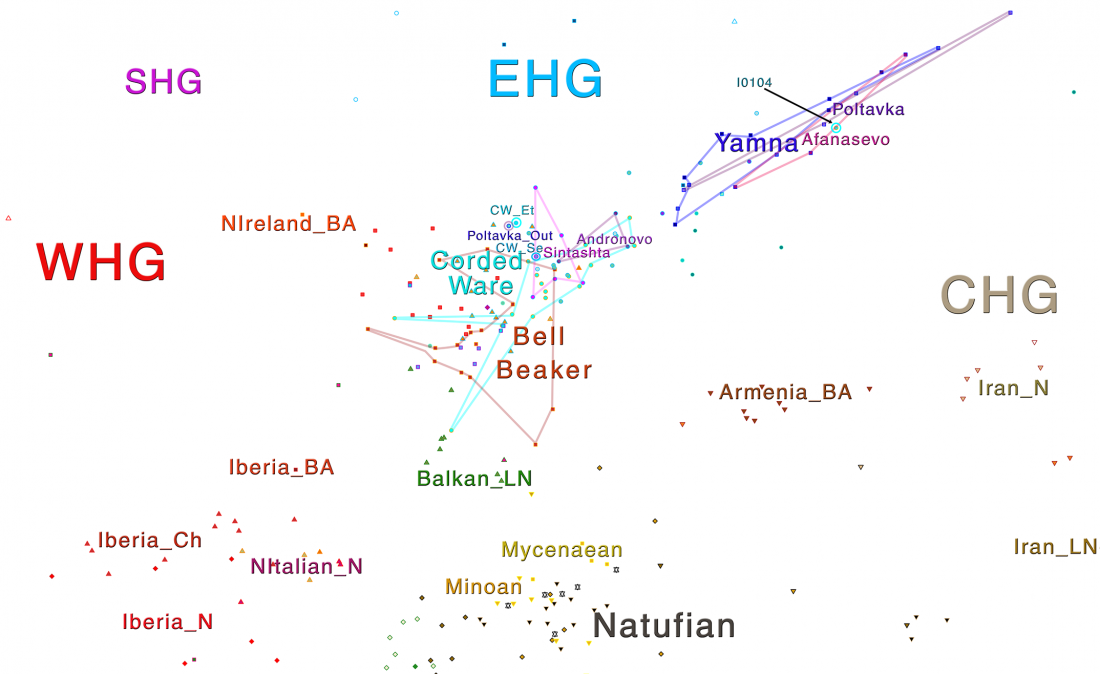
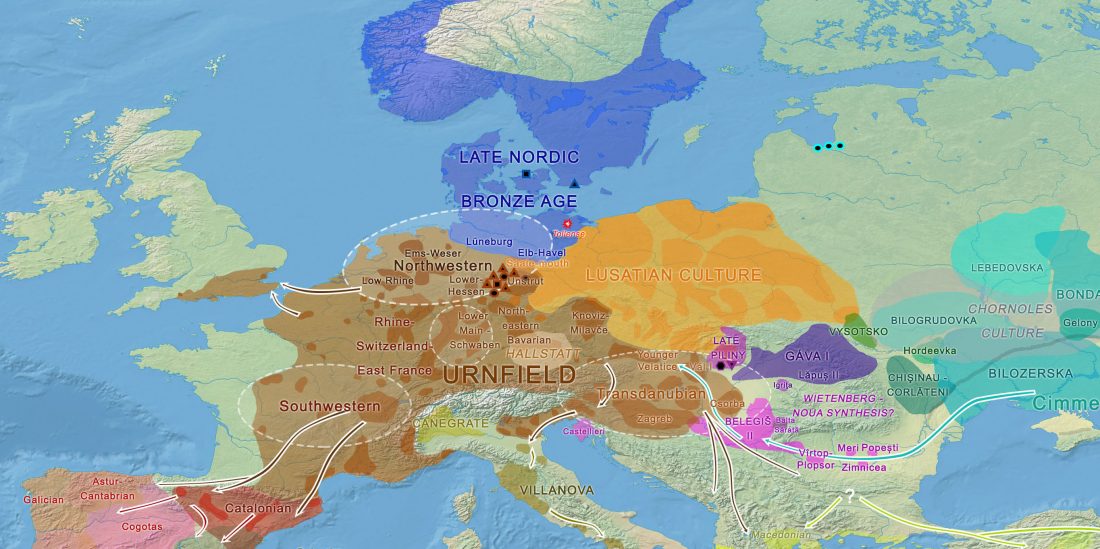
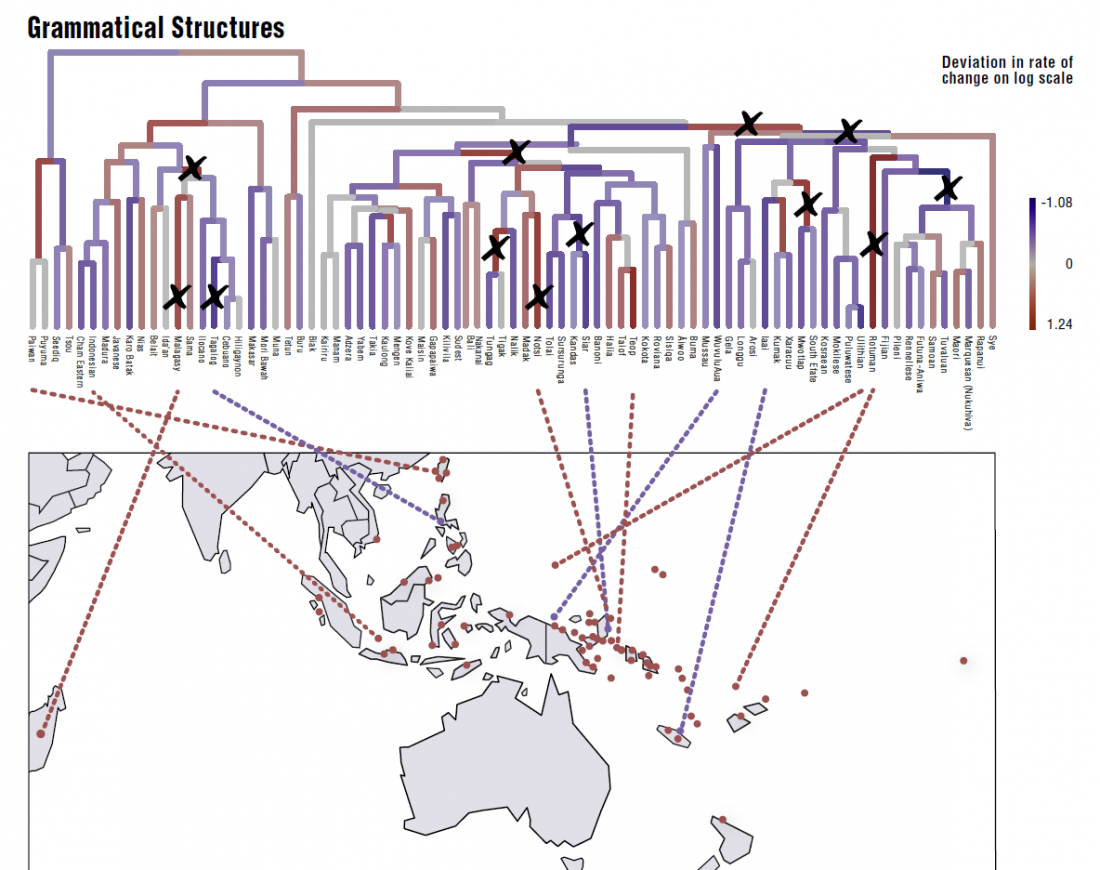
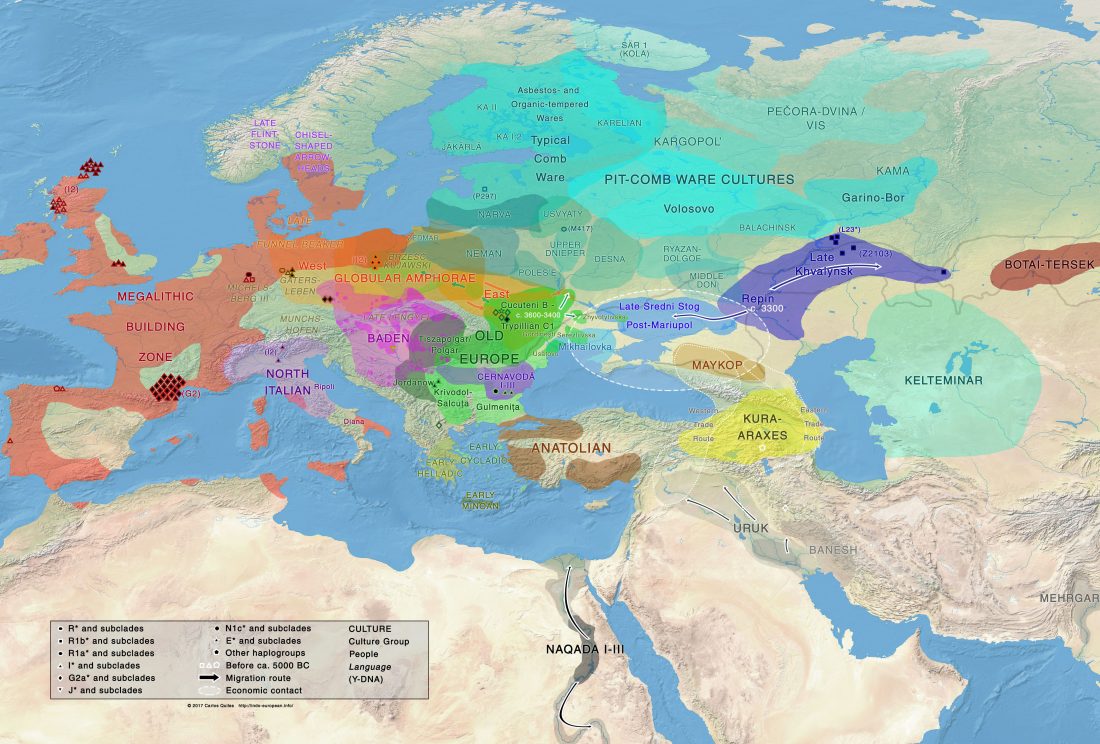
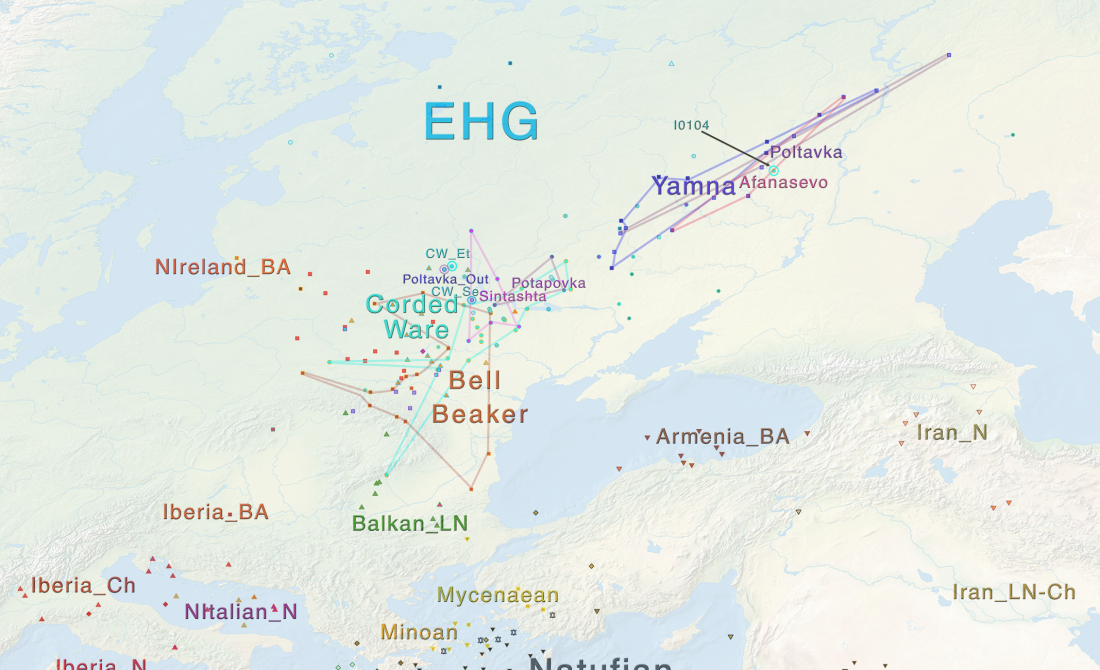
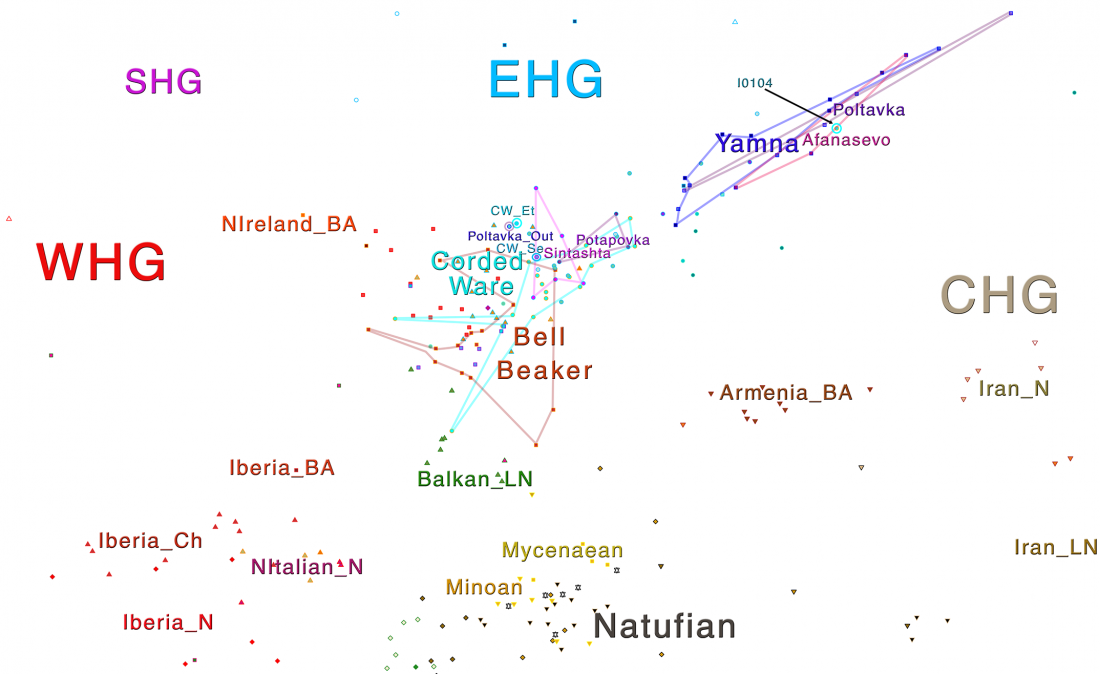
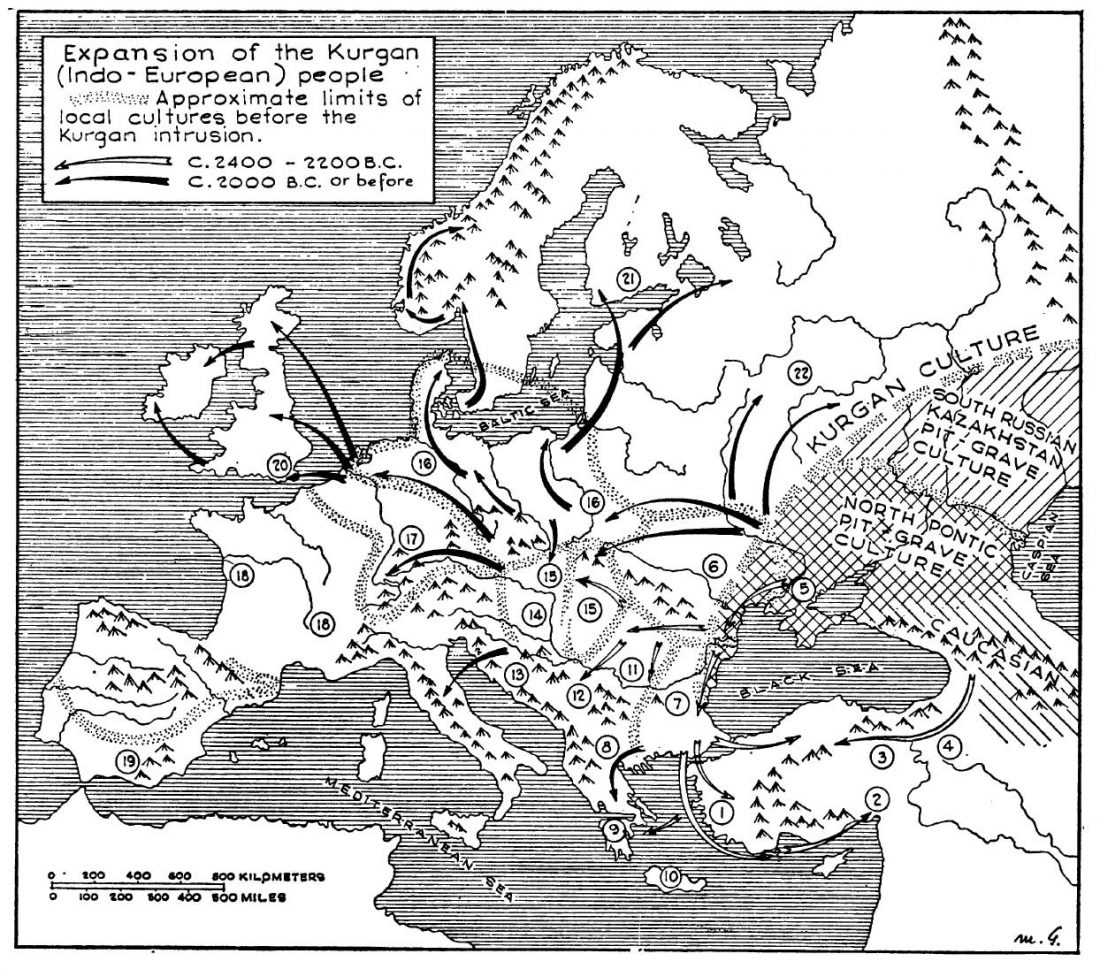
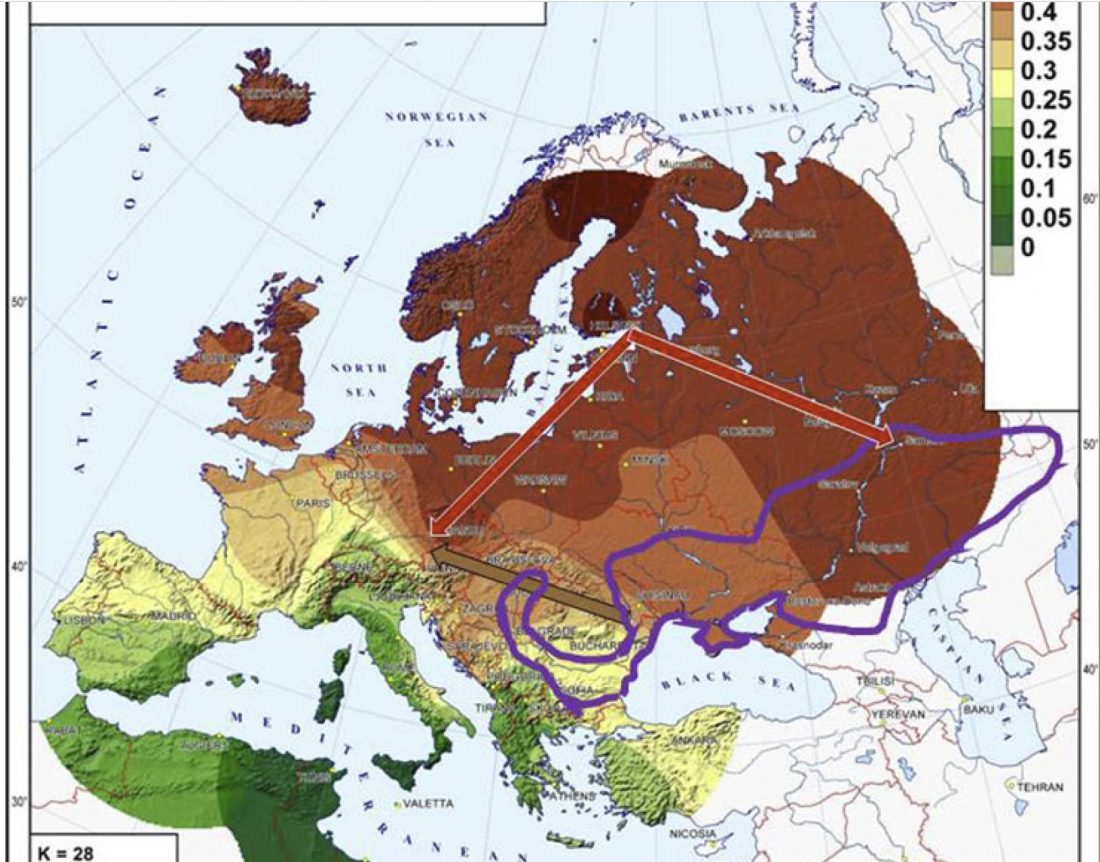
In this new version I have added more information published recently, I have updated the maps – especially the one on Palaeolithic migrations -, I have added information on Sredni Stog and its potential role in developing the Corded Ware culture and most likely language, and I have corrected certain parts that have become obsolete, especially after the latest version (19 Sept. 2017) of Mathieson et al. (2017).
It can be read or downloaded at:
- The official Wiki collaborative