Two more studies on the genetic history of East Asia: Han Chinese and Thailand
A comprehensive map of genetic variation in the world’s largest ethnic group – Han Chinese, by Charleston et al. (2017).
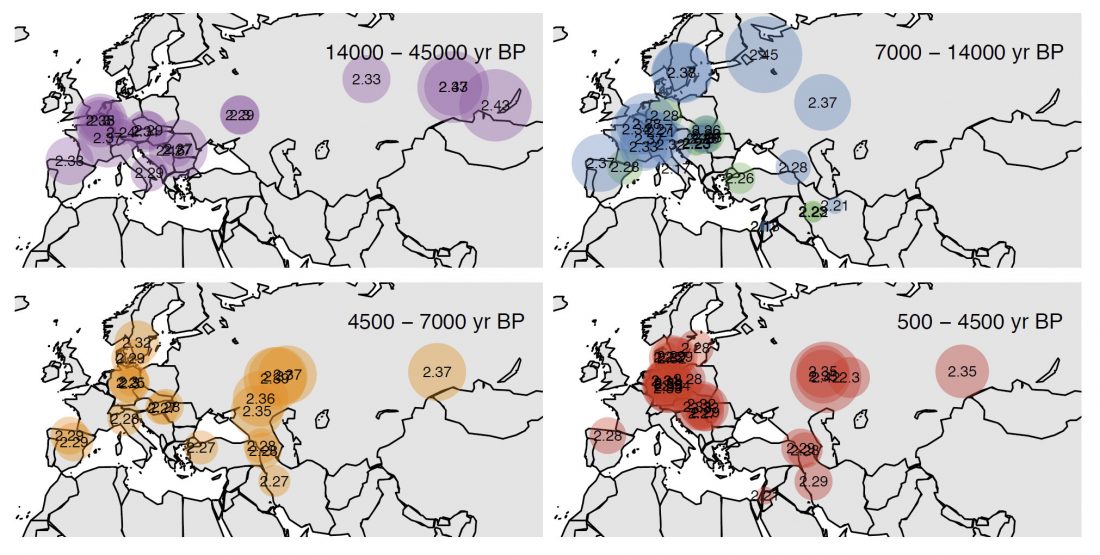
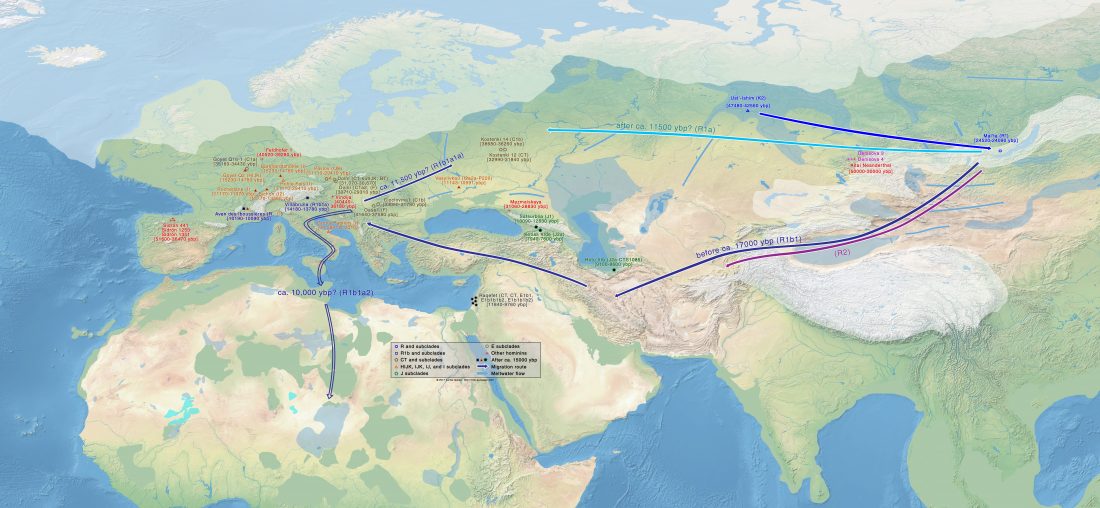
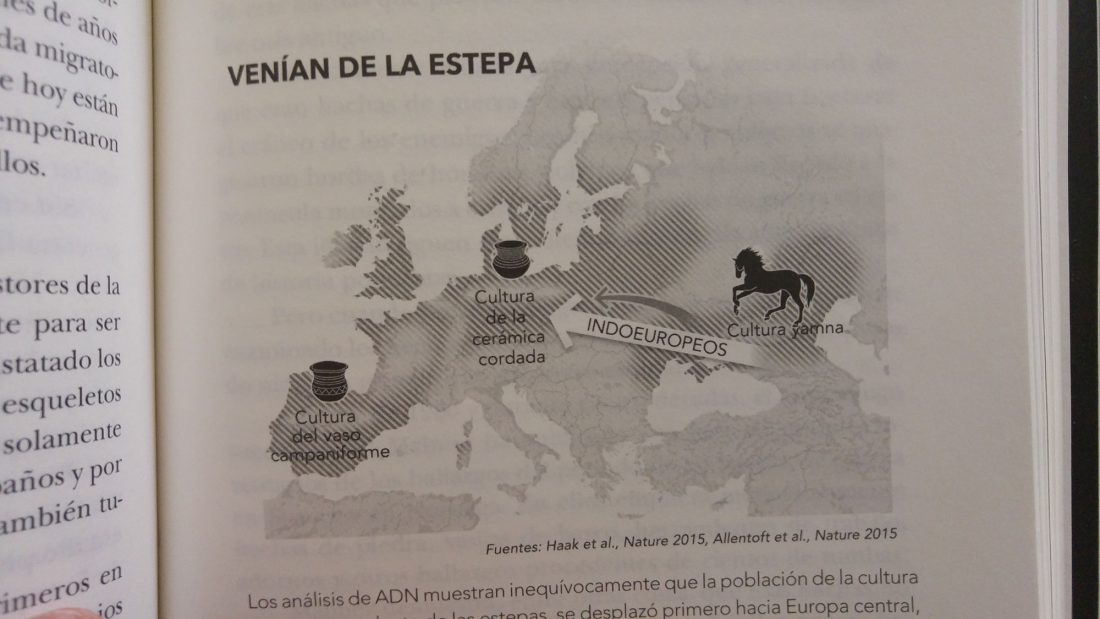
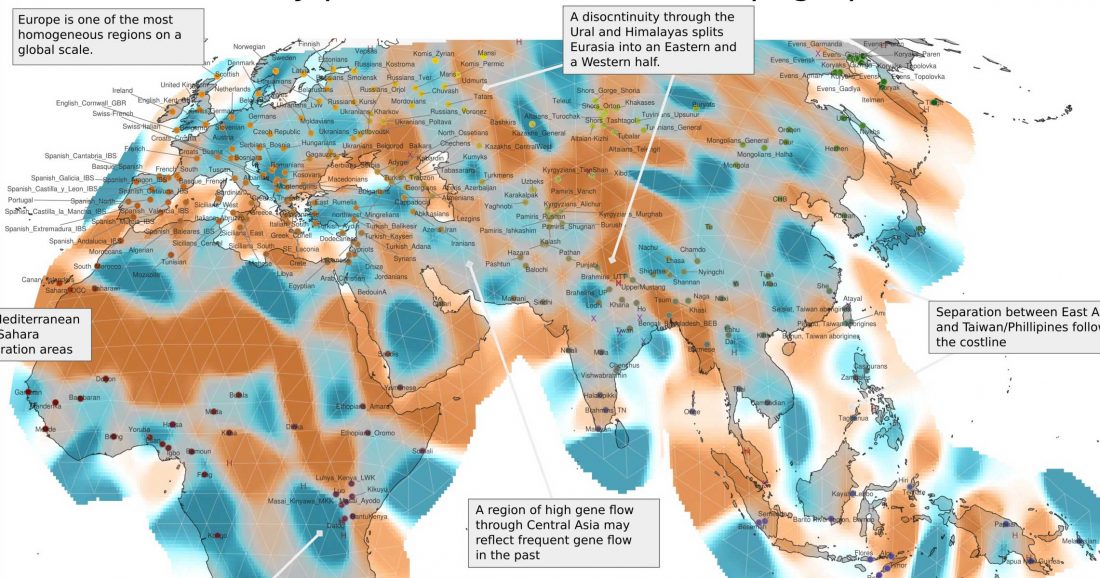
It is believed – based on uniparental markers from modern and ancient DNA samples and array-based genome-wide data – that Han Chinese originated in the Central Plain region of China during prehistoric times, expanding with agriculture and technology northward and southward, to become the largest Chinese ethnic group.
Abstract:
… Read the rest “Two more studies on the genetic history of East Asia: Han Chinese and Thailand”As are most non-European populations around the globe, the Han Chinese are relatively understudied in population and medical genetics studies. From low-coverage whole-genome sequencing of 11,670 Han Chinese women we