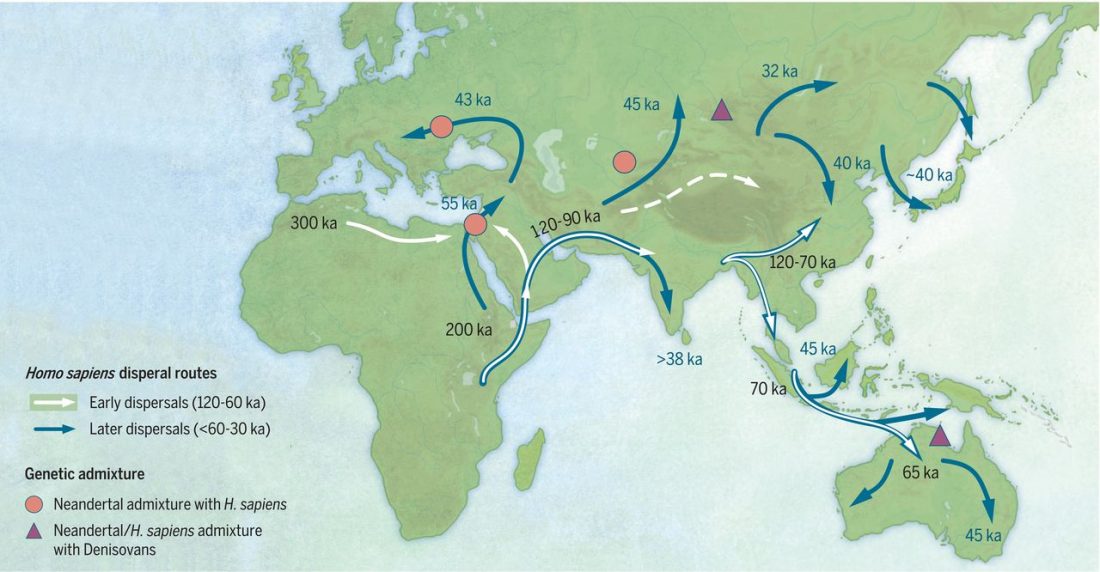
On the origin of language and human evolution
A rather risky preprint at BioRxiv, Language evolution to revolution: the jump from finite communication system with many words to infinite recursive language was associated with acquisition of mental synthesis, by Andrey Vyshedskiy (2017).
Abstract:
… Read the rest “On the origin of language and human evolution”There is overwhelming archeological and genetic evidence that modern speech apparatus was acquired by hominins by 600,000 years ago. There is also widespread agreement that behavioral modernity arose around 100,000 years ago. We attempted to answer three crucial questions: (1) what triggered the acquisition of behavioral modernity 100,000 years ago, (2) why there was a long gap between acquisition of modern speech apparatus and