Trypillia and Greece Neolithic outliers: the smoking gun of Proto-Anatolian migrations?
(Continued from the post Corded Ware culture origins: The Final Frontier).
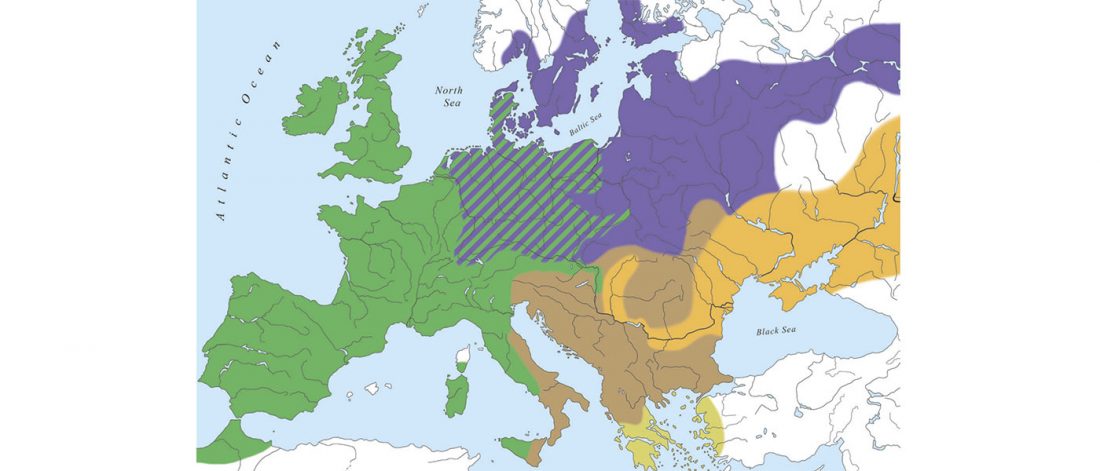
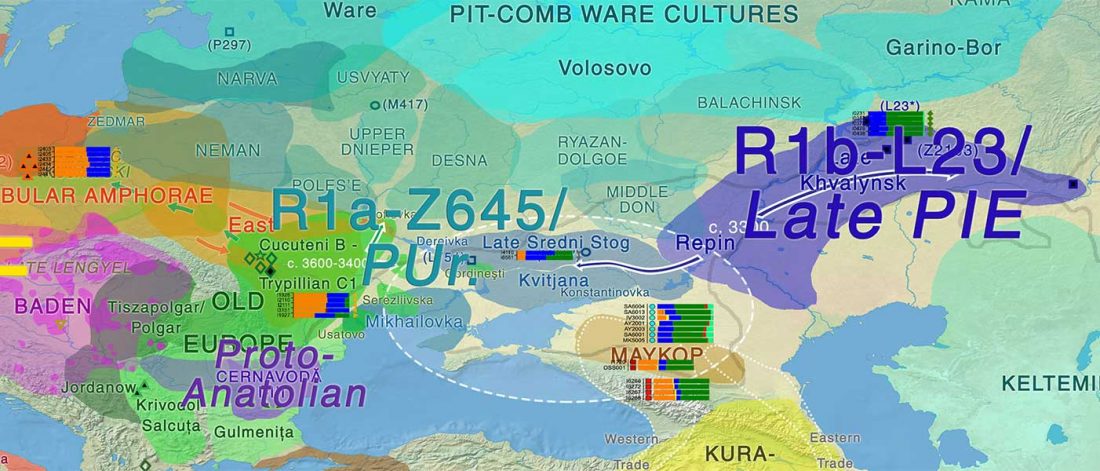
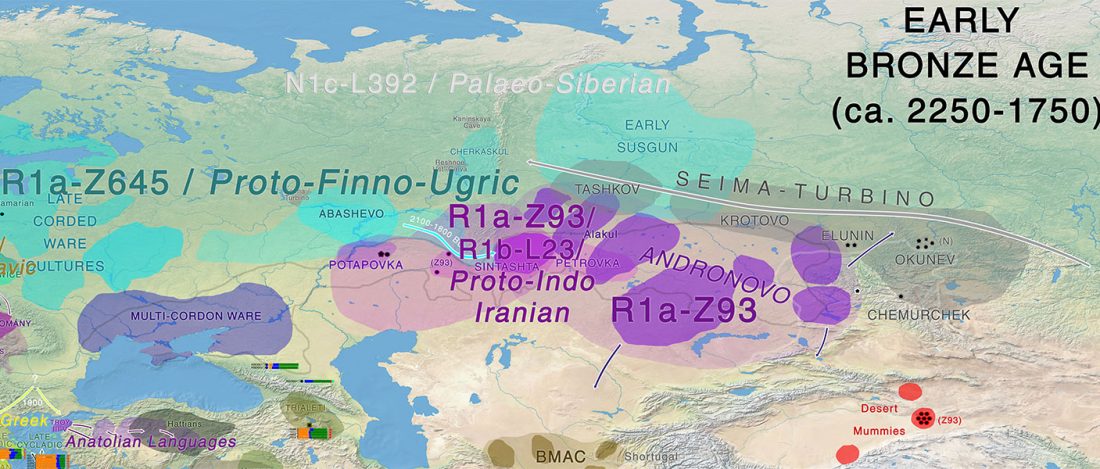
Looking at the PCA of Wang et al. (2018), I realized that Sredni Stog / Corded Ware peoples seem to lie somewhere between:
- the eastern steppe (i.e. Khvalynsk-Yamna); and
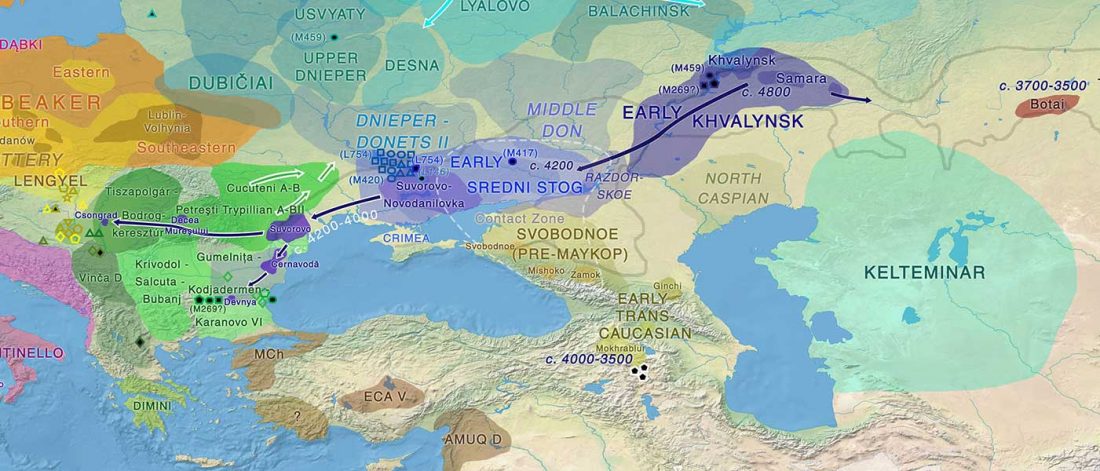
- Lower Danube and Balkan cultures affected by Anatolian- and steppe-related (i.e. Khvalynsk-Novodanilovka) migrations.
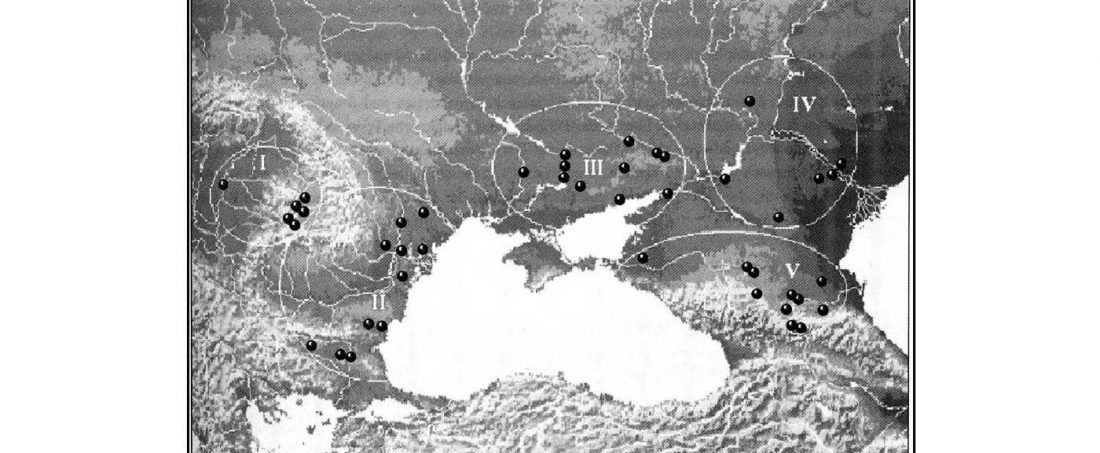
This multiethnic interaction of the western steppe fits therefore the complex archaeological description of events in the North Pontic, Lower Danube, and Dnieper-Dniester regions. Here are some interesting samples related to those long-lasting contacts:
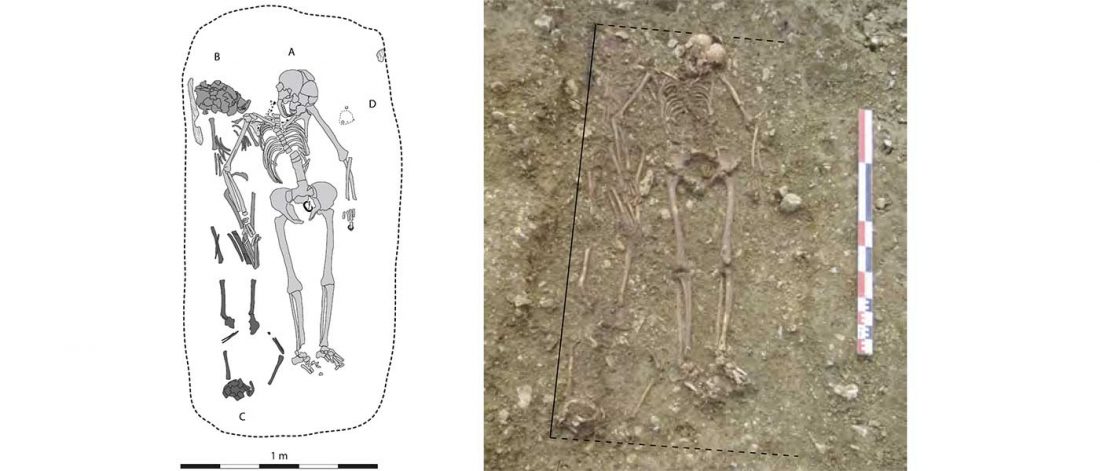
1. I3719 (mtDNA H1, Y-DNA I2a2a) Ukraine Neolithic sample … Read the rest “Trypillia and Greece Neolithic outliers: the smoking gun of Proto-Anatolian migrations?”