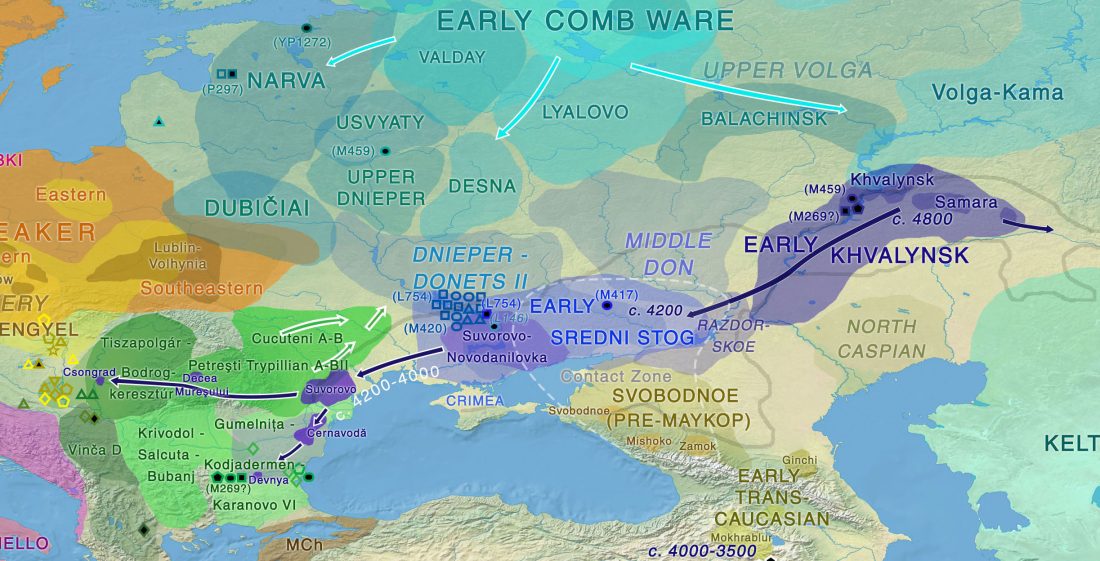
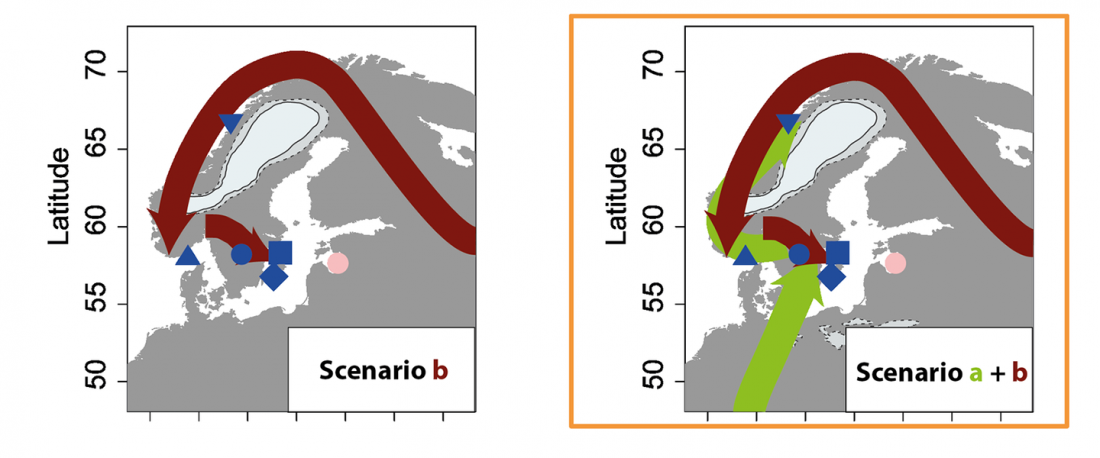
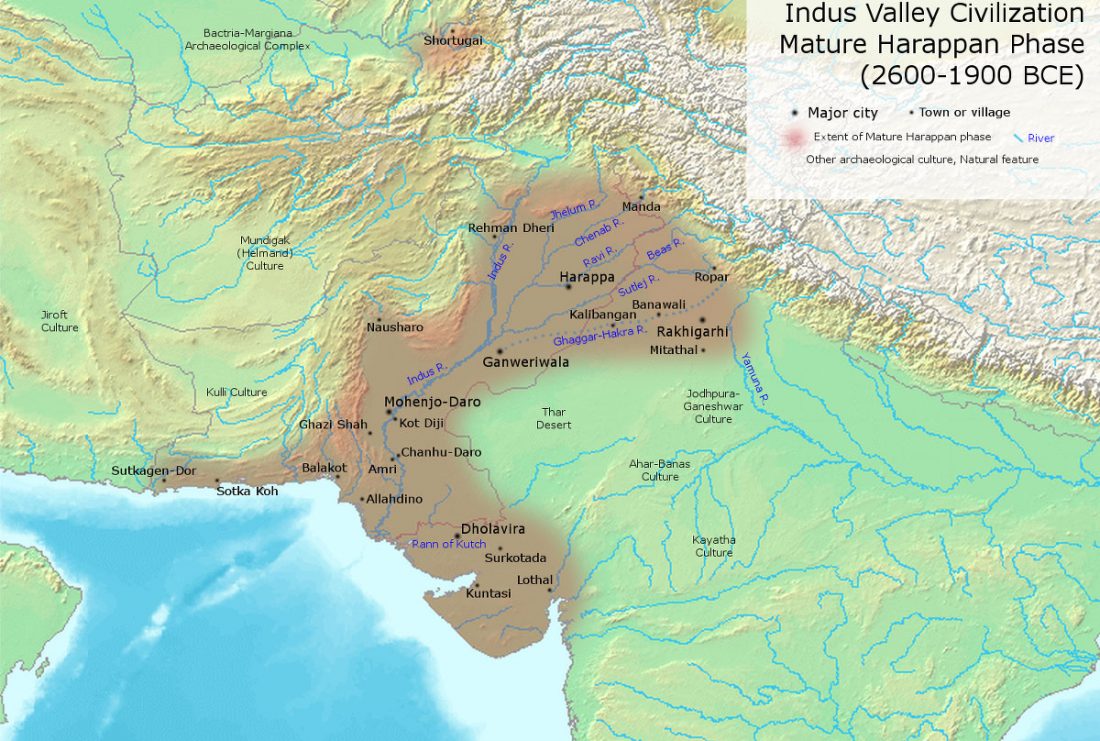
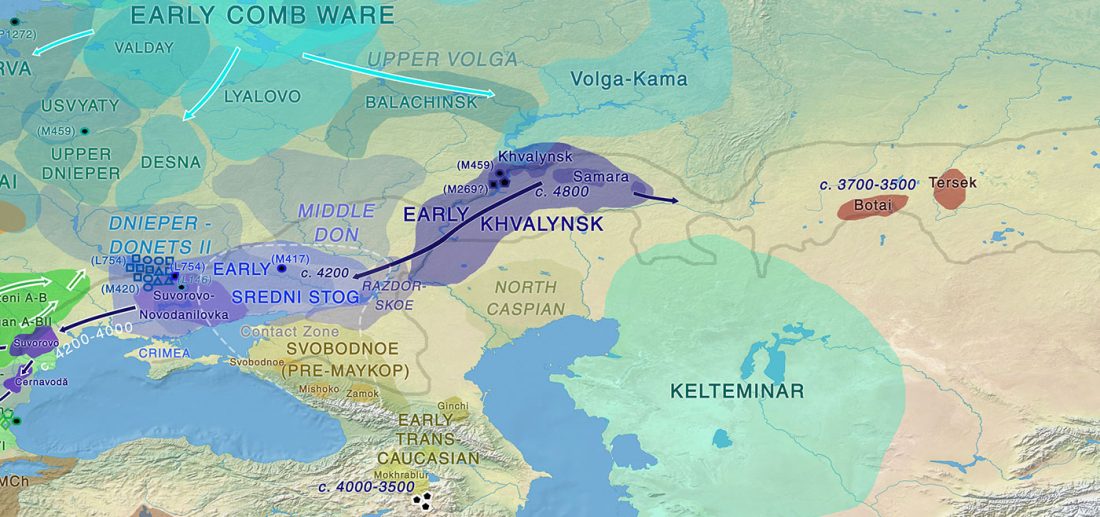
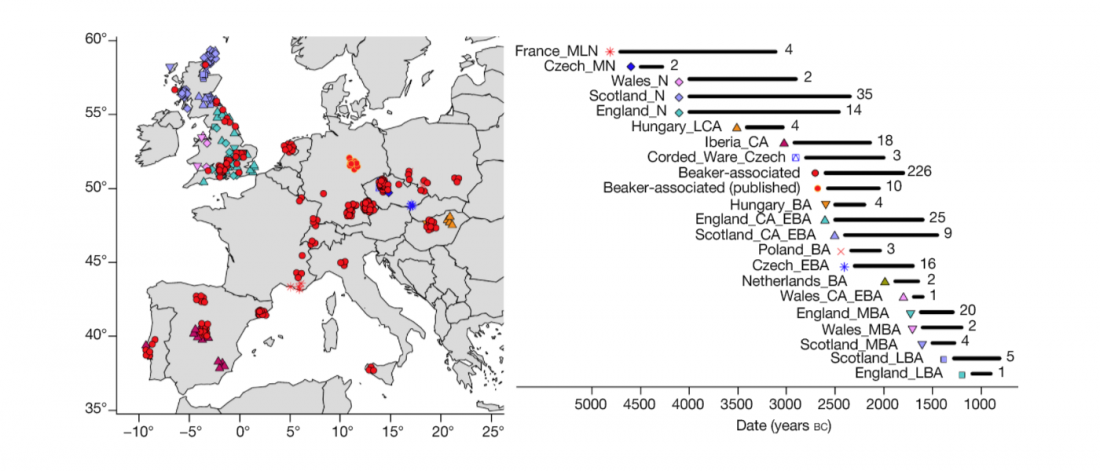
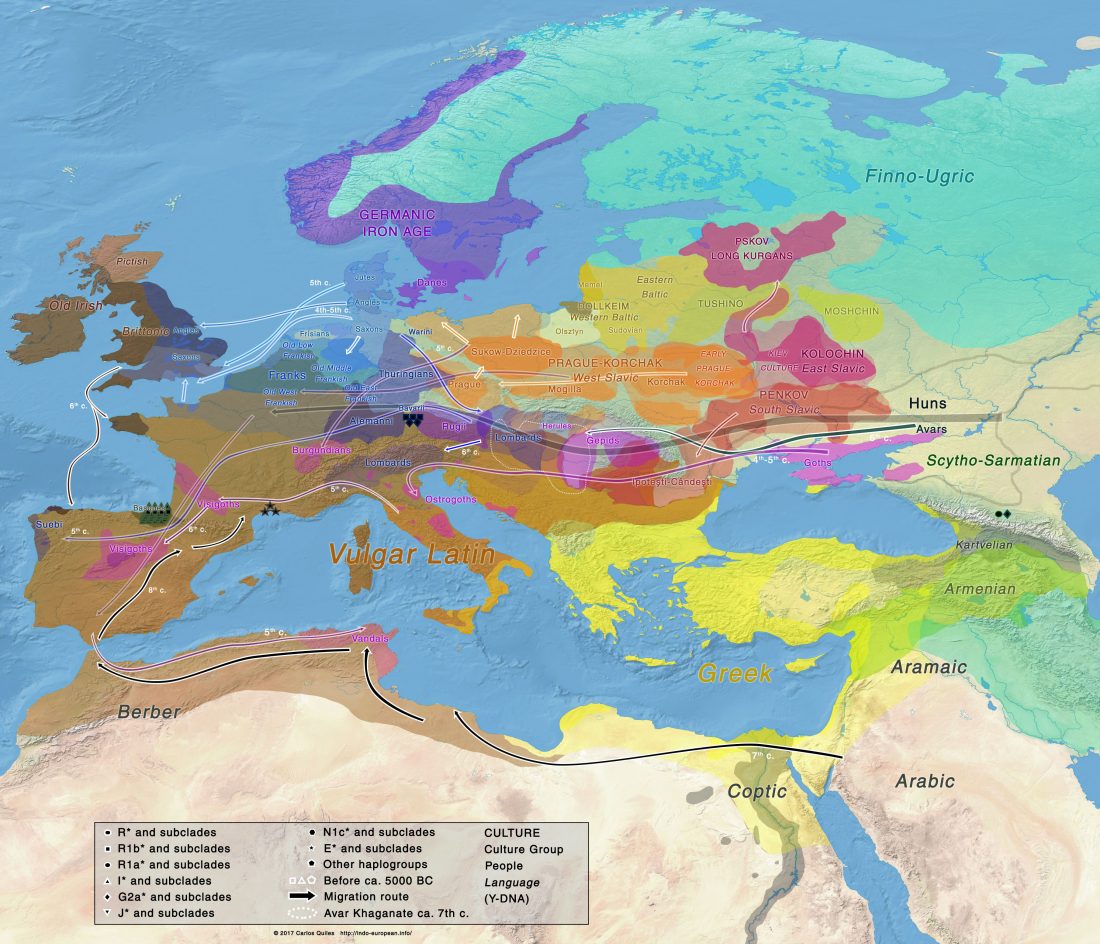
Consequences of O&M 2018 (II): The unsolved nature of Suvorovo-Novodanilovka chiefs, and the route of Proto-Anatolian expansion
This is part of a series of posts analyzing the findings of the recent Nature papers Olalde et al.(2018) and Mathieson et al.(2018) (abbreviated O&M 2018).
I already expressed my predictions for 2018. One of the most interesting questions among them is the identification of the early Anatolian offshoot, and this is – I believe – where Genomics has the most to say in Indo-European migrations.
Linguistics and Archaeology had already a mainstream account from Late PIE/Yamna onwards, and it has been proven right in Genomic investigation. There is, however, no consensus on Indo-Hittite.