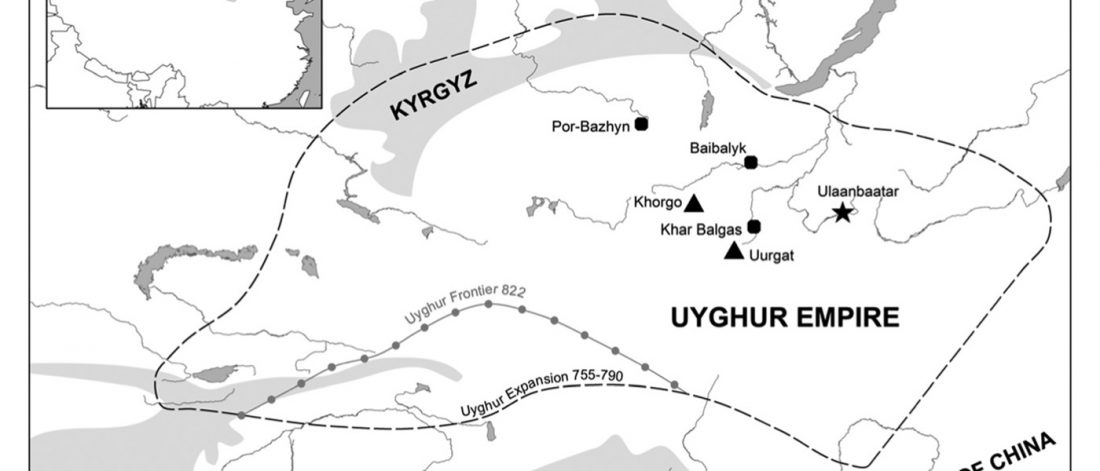
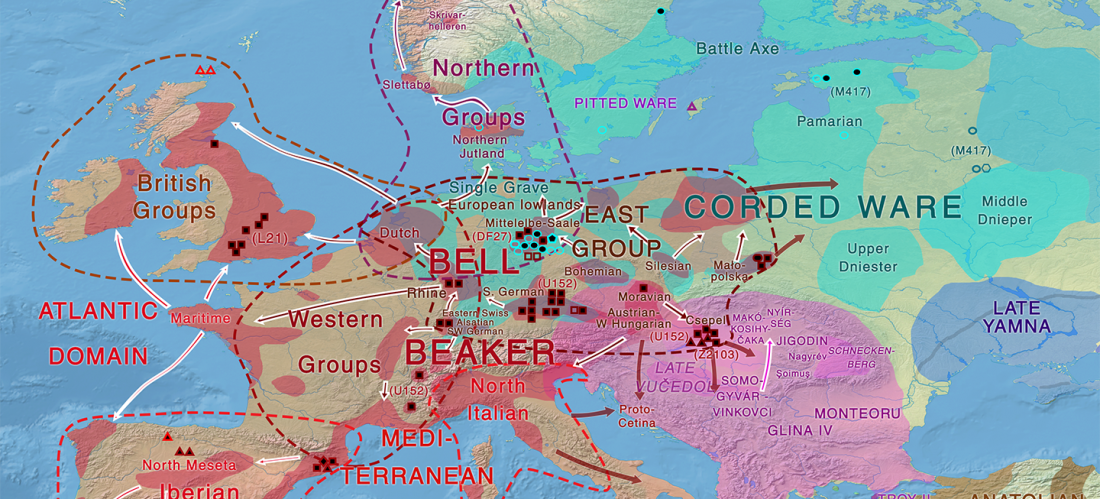
How an empire of steppe nomads coped with environmental stress
Recent paper (behind paywall), Environmental Stress and Steppe Nomads: Rethinking the History of the Uyghur Empire (744–840) with Paleoclimate Data, by Di Cosmo et al. JINH (2018) XLVIII(4):439-463.
Abstract (emphasis mine):
… Read the rest “How an empire of steppe nomads coped with environmental stress”Newly available paleoclimate data and a re-evaluation of the historical and archaeological evidence regarding the Uyghur Empire (744–840)—one of several nomadic empires to emerge on the Inner Asian steppe—suggests that the assumption of a direct causal link between drought and the stability of nomadic societies is not always justified. The fact that a severe drought lasting nearly seven decades did not cause the Uyghur Empire to collapse, to