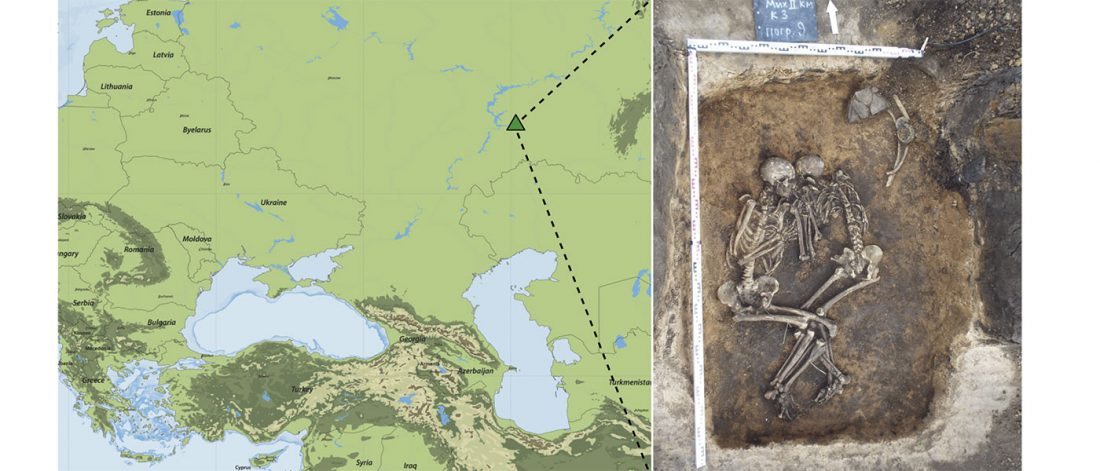
Open access Emergence and Spread of Basal Lineages of Yersinia pestis during the Neolithic Decline, by Rascovan et al. Cell (2018)
Abstract (emphasis mine):
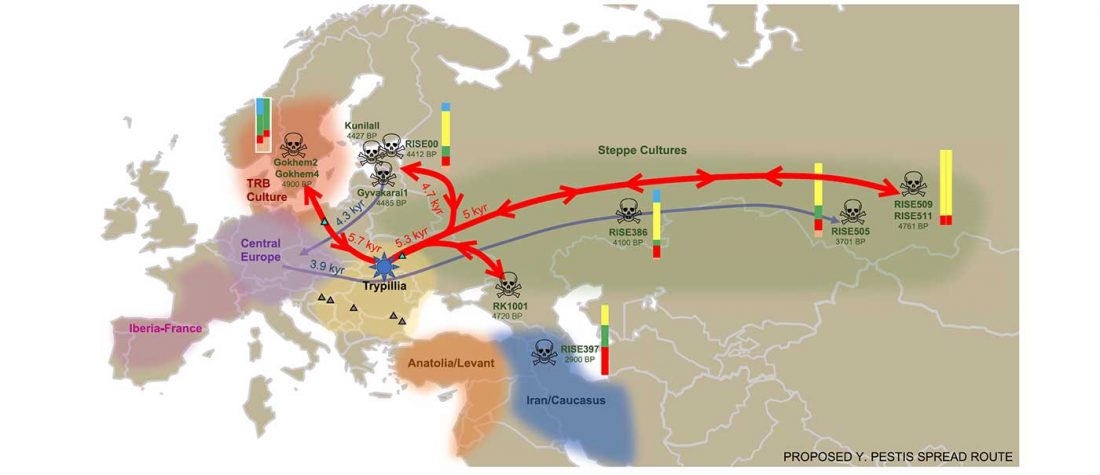
… Read the rest “Spread of Y. pestis, earlier than previously thought, may have caused Neolithic decline”Between 5,000 and 6,000 years ago, many Neolithic societies declined throughout western Eurasia due to a combination of factors that are still largely debated. Here, we report the discovery and genome reconstruction of Yersinia pestis, the etiological agent of plague, in Neolithic farmers in Sweden, pre-dating and basal to all modern and ancient known strains of this pathogen. We investigated the history of this strain by combining phylogenetic and molecular clock analyses of the bacterial