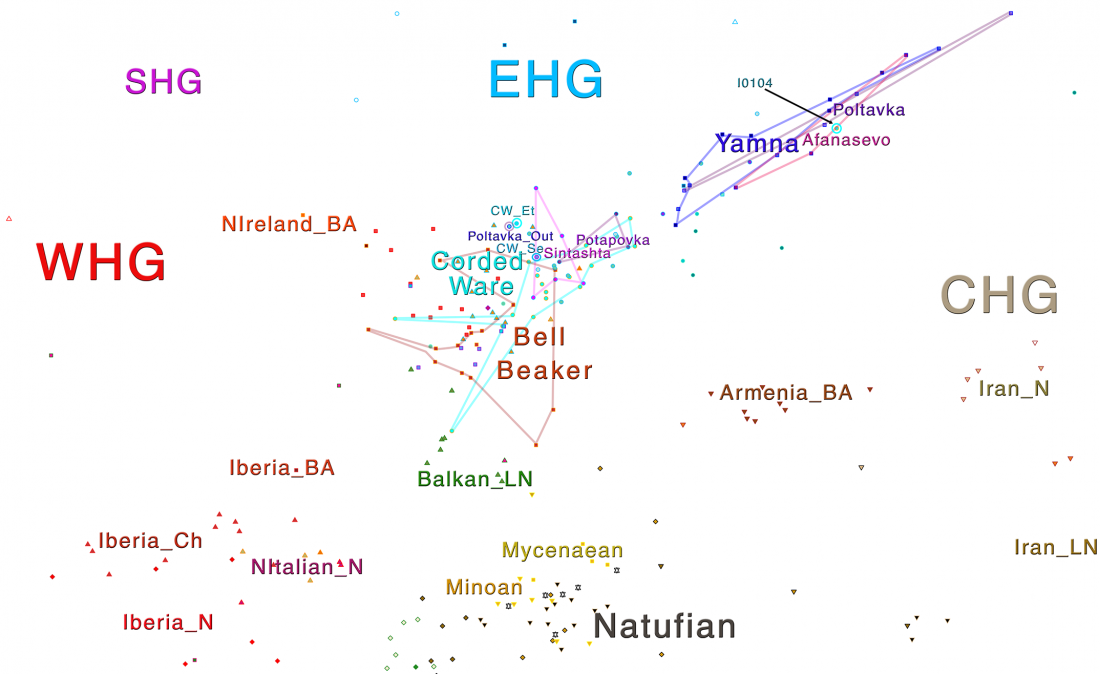
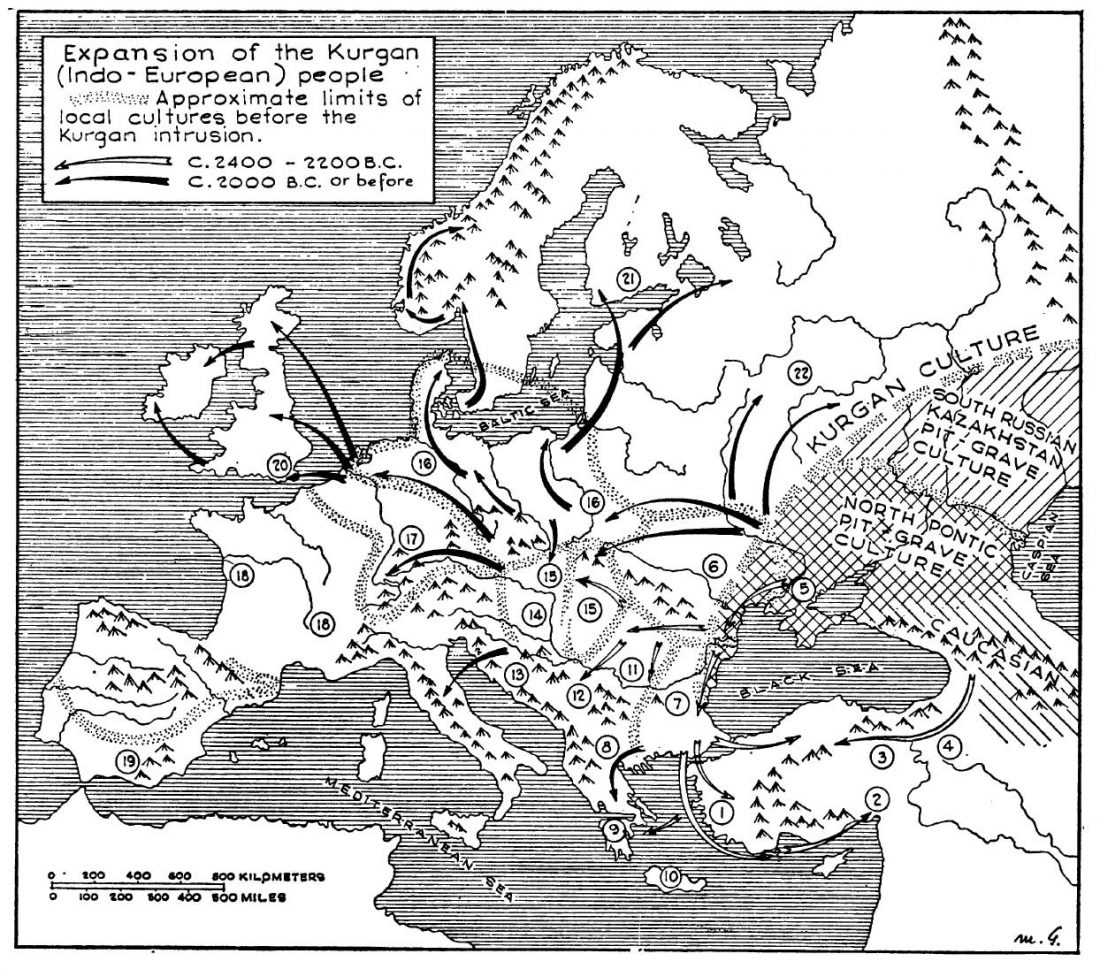
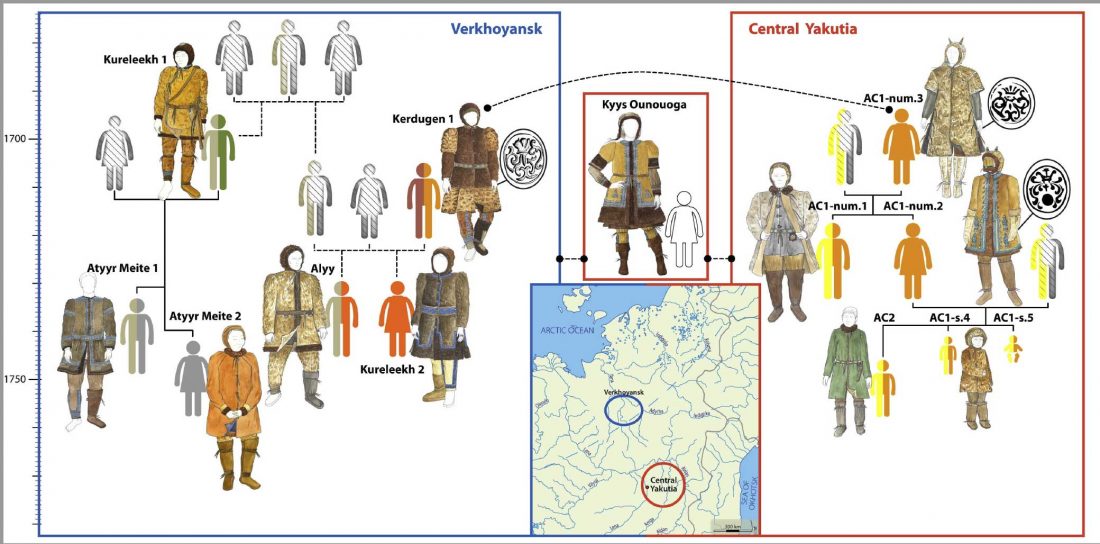
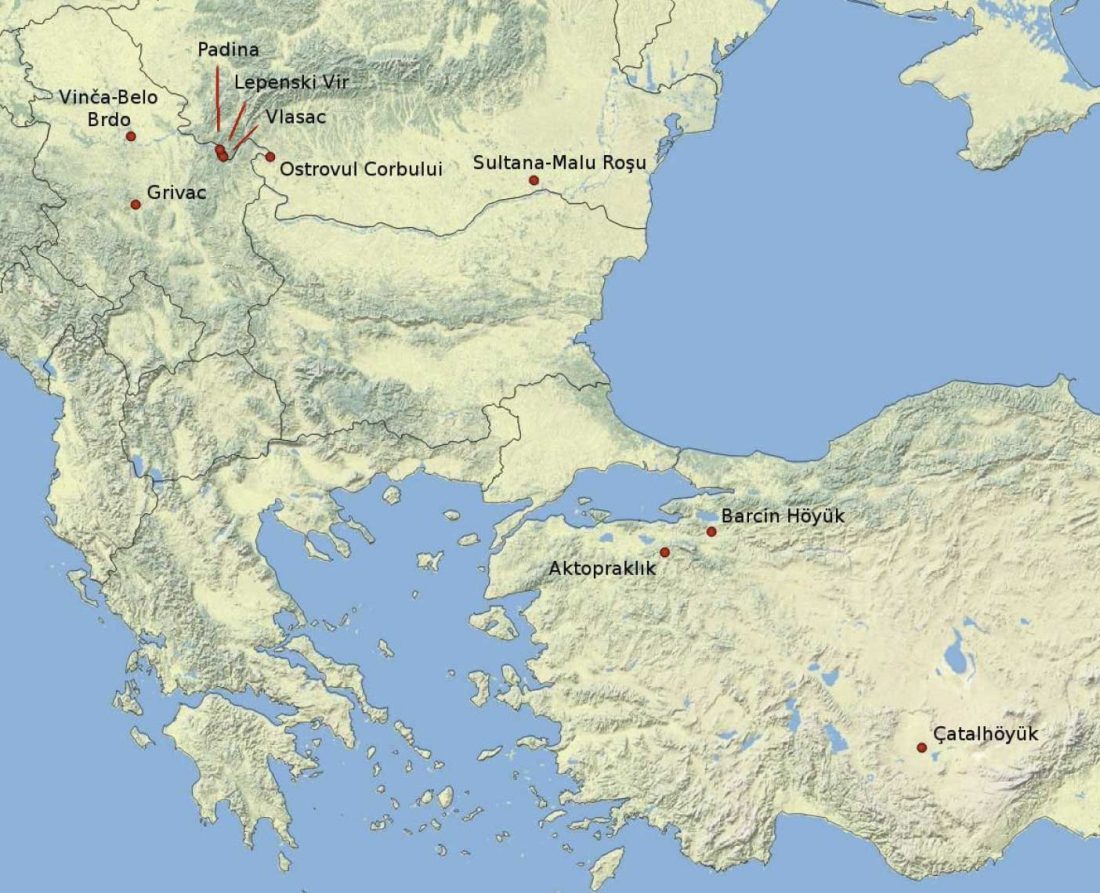
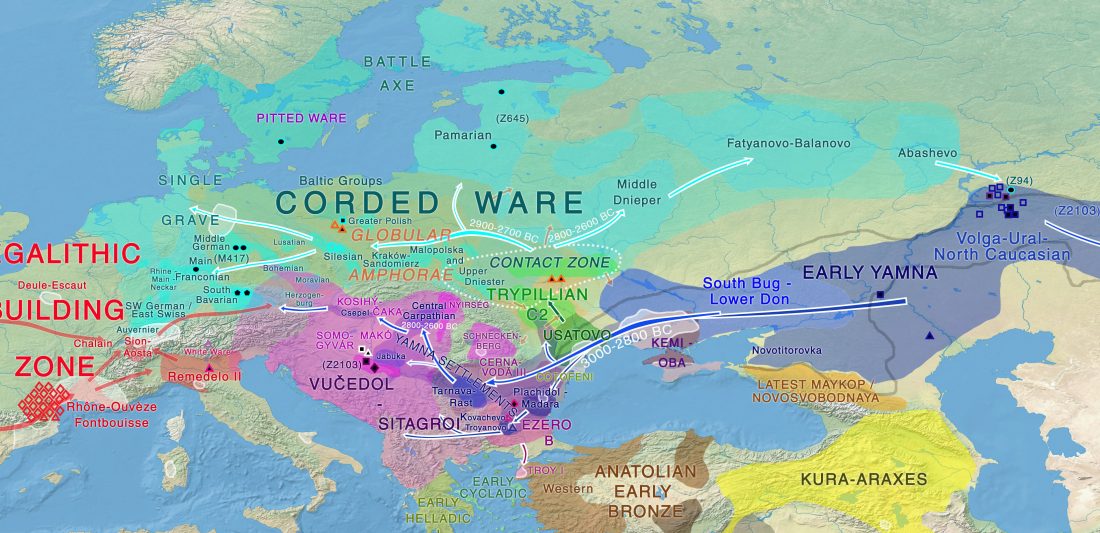
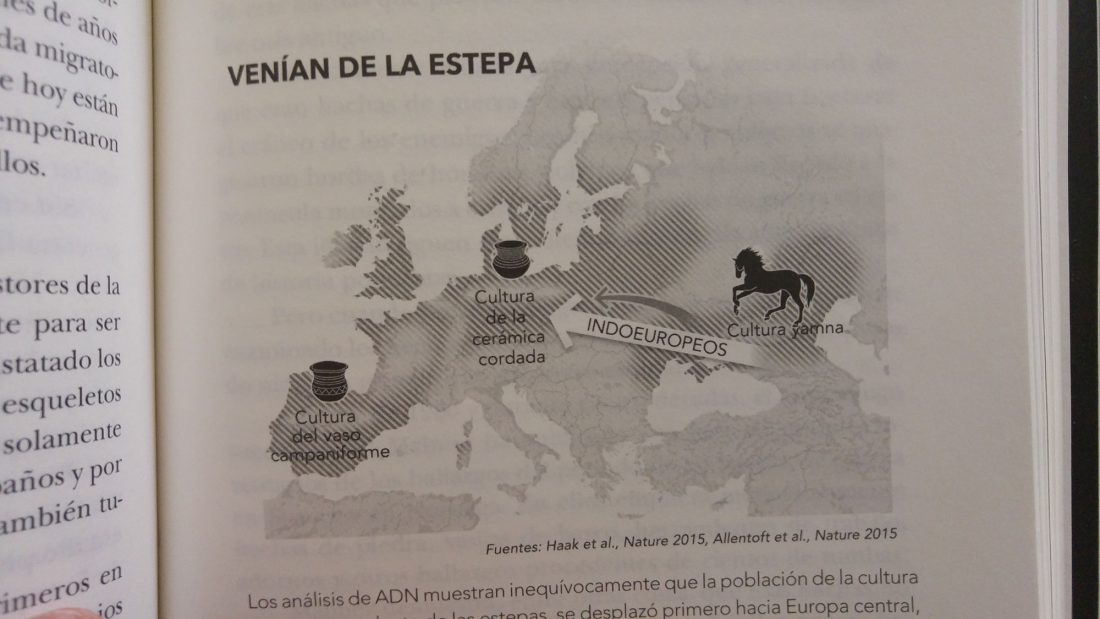
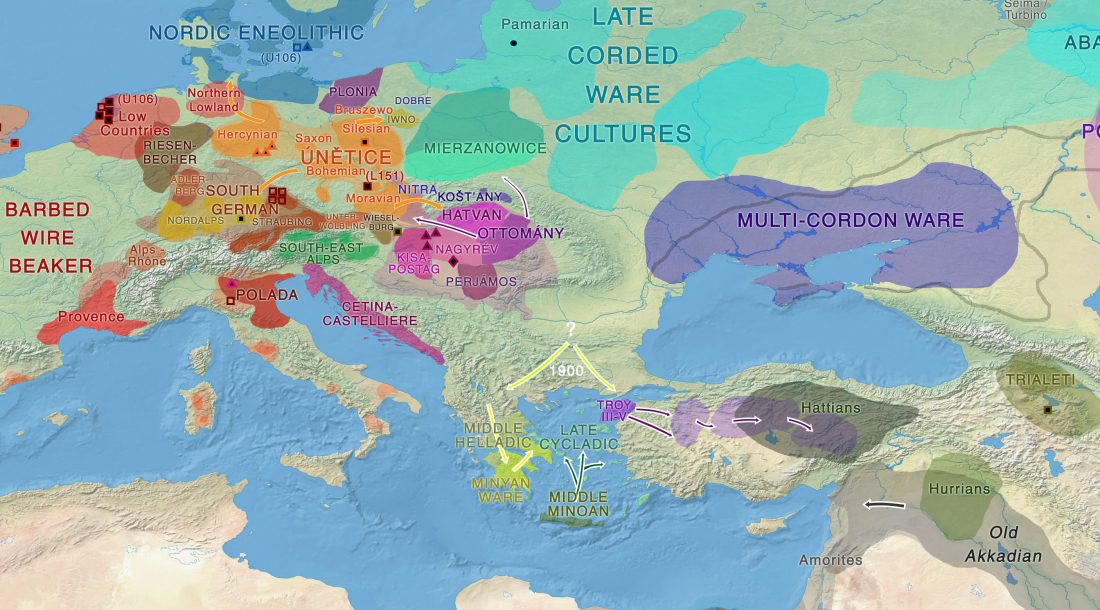
I have just uploaded the working draft of the third version of the Indo-European demic diffusion model. Unlike the previous two versions, which were published as essays (fully developed papers), this new version adds more information on human admixture, and probably needs important corrections before a definitive edition can be published.
The third version is available right now on ResearchGate and Academia.edu. I will post the PDF at Academia Prisca, as soon as possible:
- Read or download at Academia.edu
- Read or download at ResearchGate
- [EDIT 21 September 2017:] Download in PDF from indo-european.info
Feel free to … Read the rest “Indo-European demic diffusion model, 3rd edition”