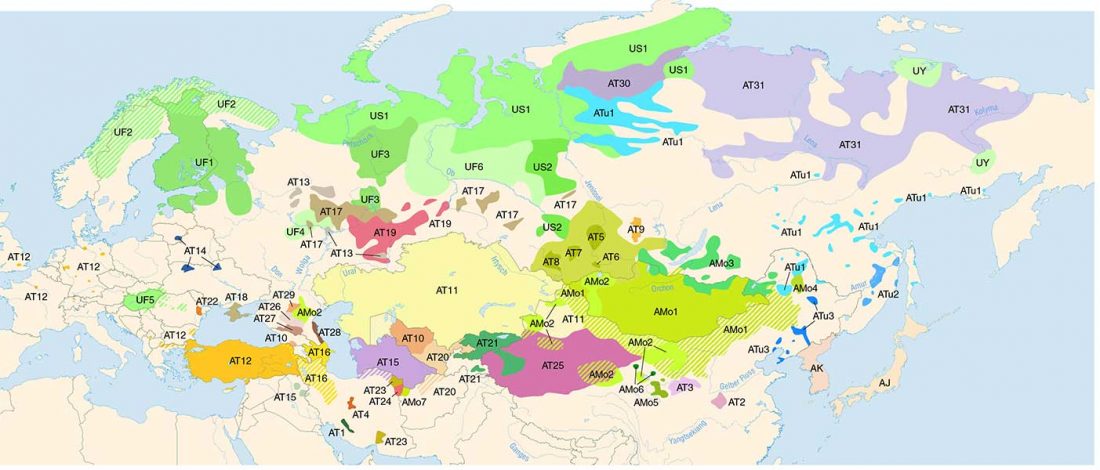
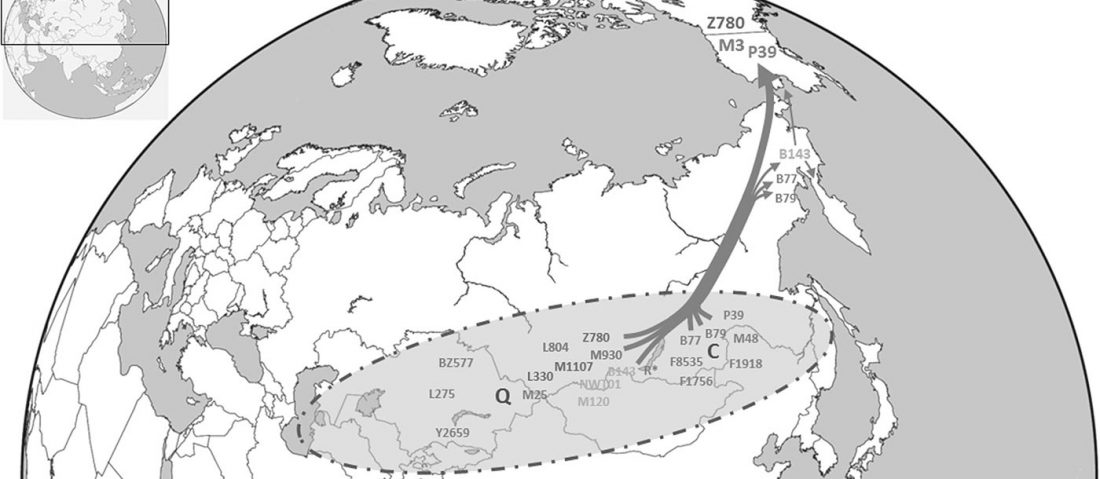
Open access Estimating the impact of the Mongol expansion upon the gene pool of Tuvans, by Balanovskaya et al., Vavilov Journal of genetics and breeding (2018), 22(5):611-619.
Abstract (emphasis mine):
… Read the rest “Y-DNA haplogroups of Tuvinian tribes show little effect of the Mongol expansion”With a view to trace the Mongol expansion in Tuvinian gene pool we studied two largest Tuvinian clans – those in which, according to data of humanities, one could expect the highest Central Asian ancestry, connected with the Mongol expansion. Thus, the results of Central Asian ancestry in these two clans component may be used as upper limit of the Mongol influence upon the Tuvinian gene pool in a