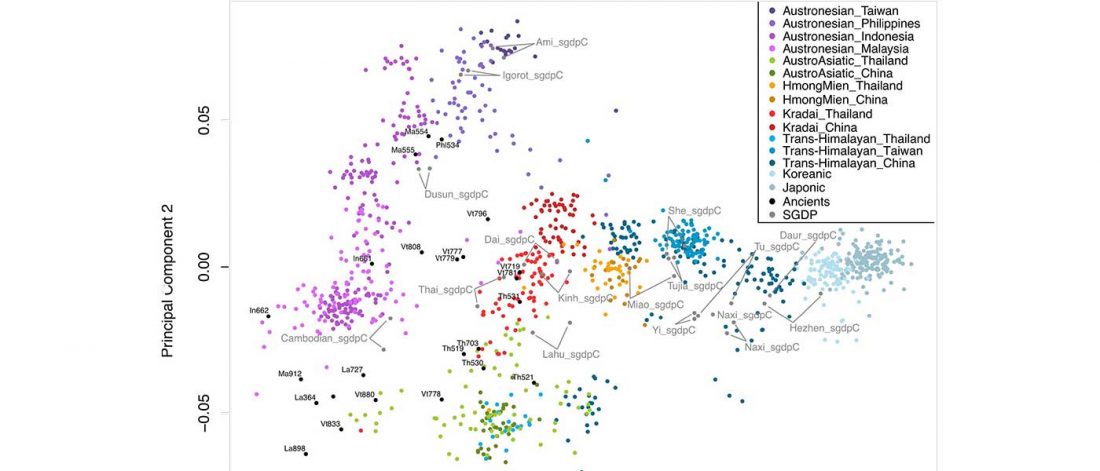
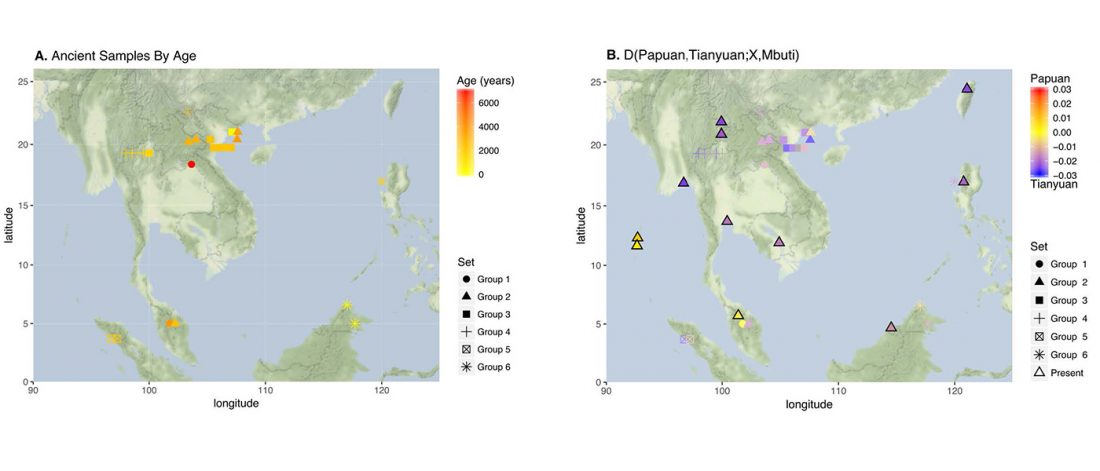
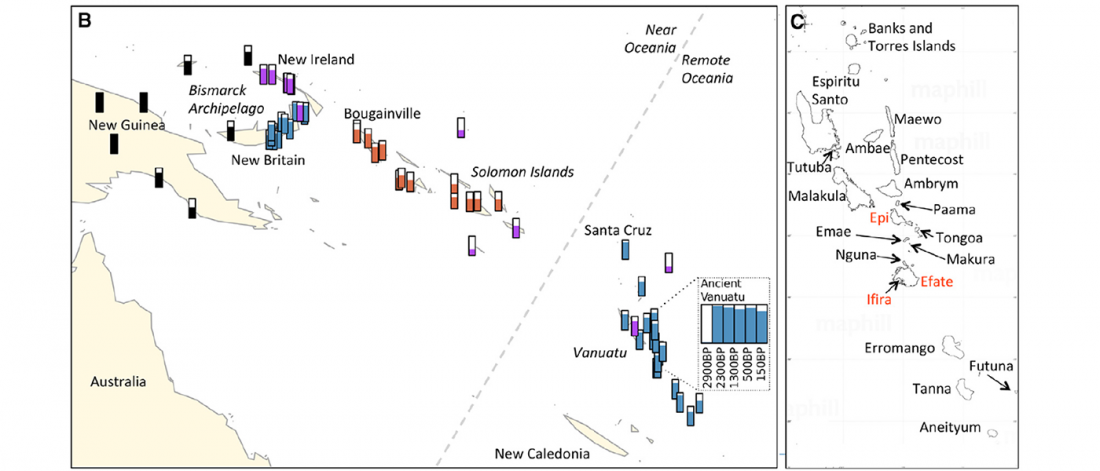
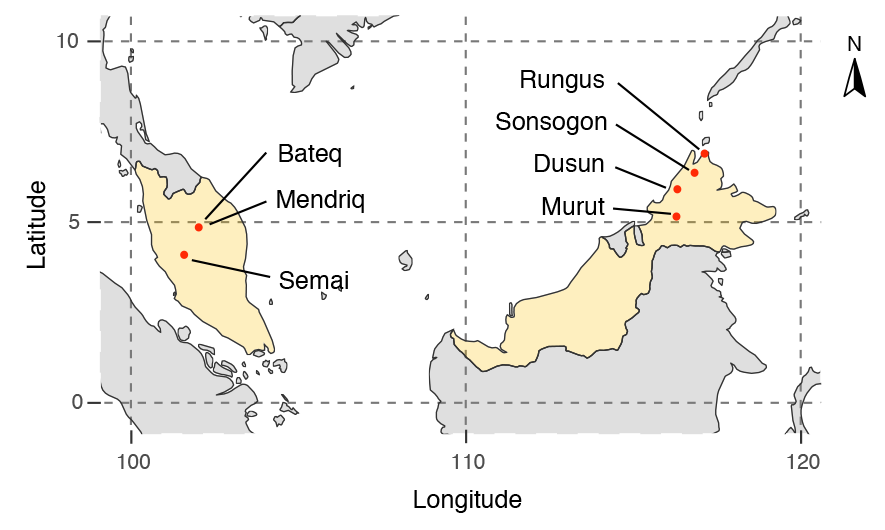
New paper (behind paywall) The prehistoric peopling of Southeast Asia, by McColl et al. (Science 2018) 361(6397):88-92 from a recent bioRxiv preprint.
Interesting is this apparently newly reported information including a female sample from the Ikawazu Jōmon of Japan ca. 570 BC (emphasis mine):
… Read the rest “South-East Asia samples include shared ancestry with Jōmon”The two oldest samples — Hòabìnhians from Pha Faen, Laos [La368; 7950 with 7795 calendar years before the present (cal B.P.)] and Gua Cha, Malaysia (Ma911; 4415 to 4160 cal B.P.)—henceforth labeled “group 1,” cluster most closely with present-day Önge from the Andaman Islands and away from other East Asian and Southeast-Asian populations (Fig.