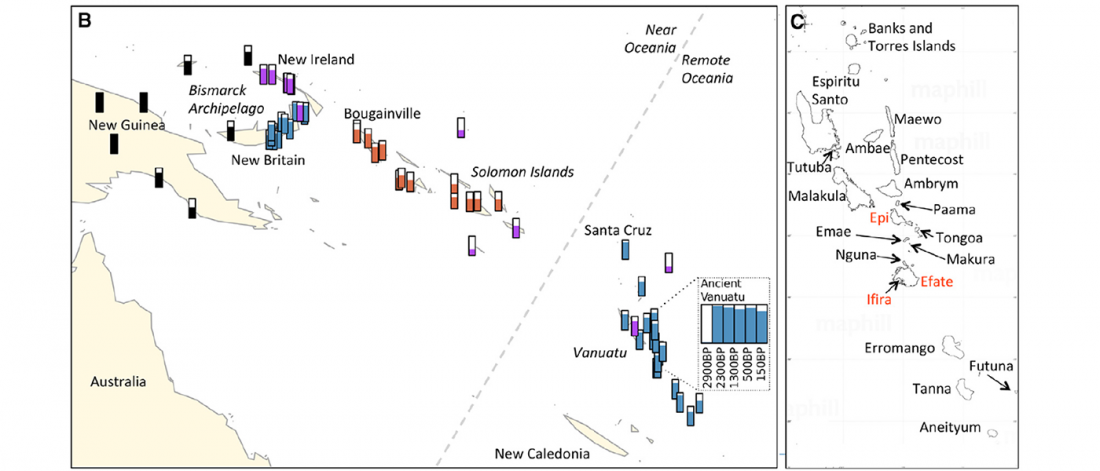
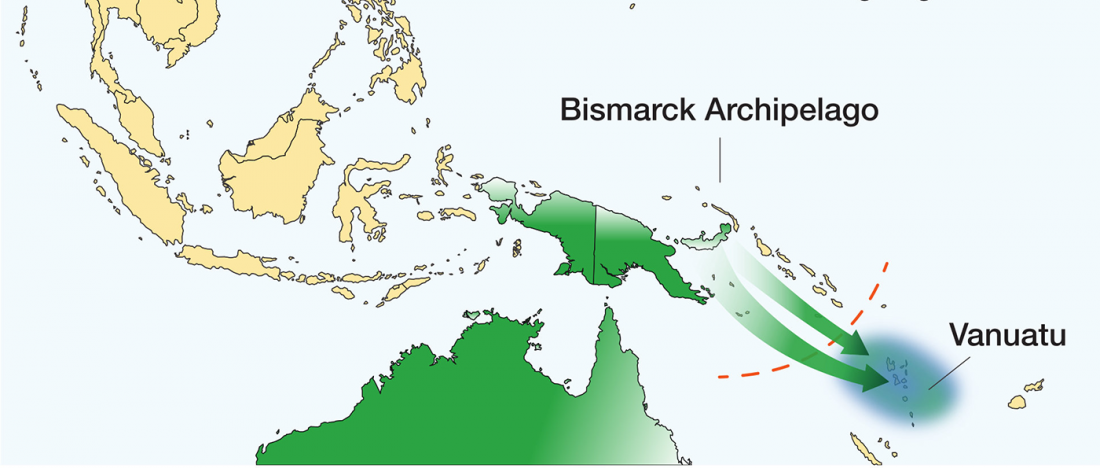
Review of recent papers on East Asia, quite relevant these days: Human Genetics: Busy Subway Networks in Remote Oceania? by Anders Bergström & Chris Tyler-Smith, Current Biology (2018) 28.
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
Ancient DNA is transforming our understanding of the human past by forcing geneticists to confront its real complexity [1]. Historians and archaeologists have long known that the development of human societies was complex and often haphazard, but geneticists have persistently tried to explain present-day patterns of genetic variation using simple models.
… Read the rest “Linguistic continuity despite genetic replacement in Remote Oceania”Early genetic analyses of present-day populations revealed a mix of Asian (Taiwanese) and Papuan (New