Interesting PhD thesis The Stone Age of north-eastern Europe 5500–1800 calBC : bridging the gap between the East and the West by Kerkko Nordqvist (2018).
Some interesting excerpts:
On the Corded Ware and related cultures
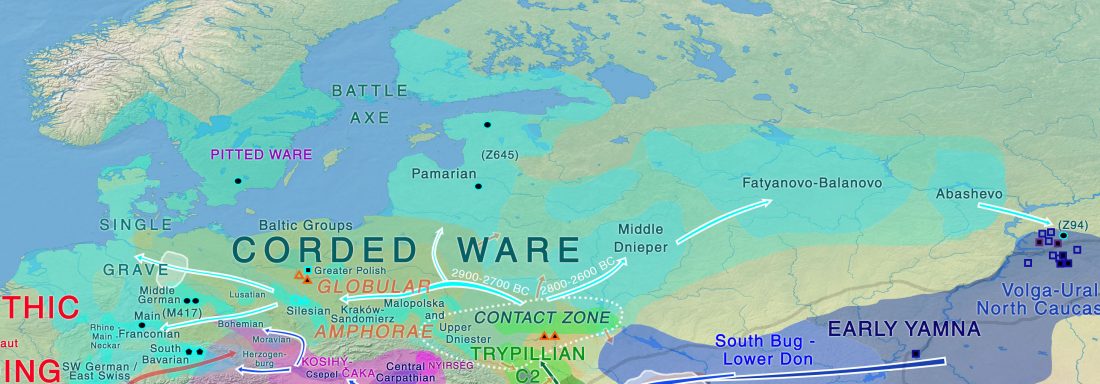
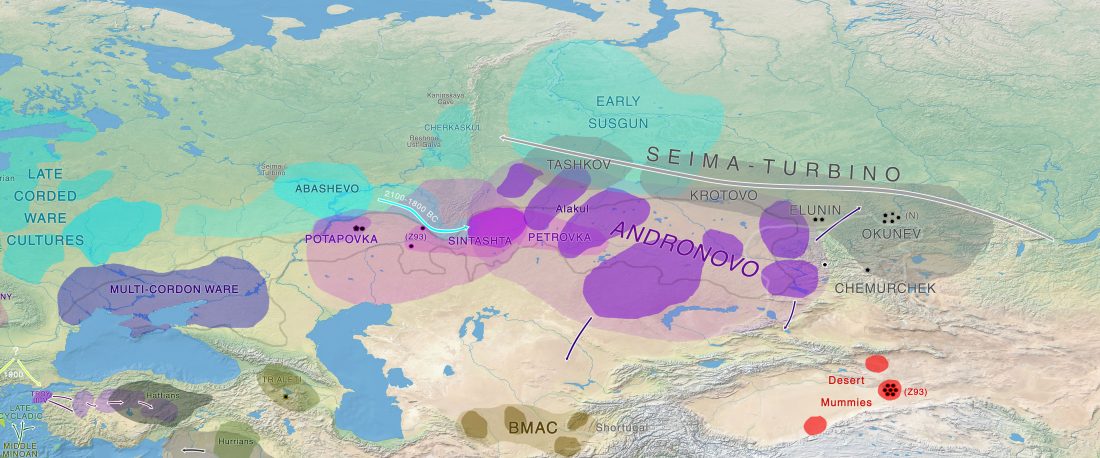
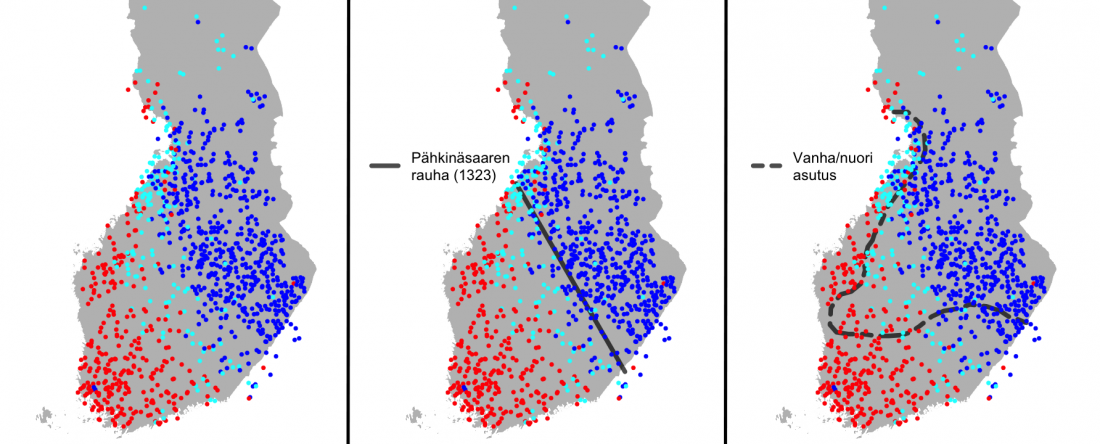
… Read the rest “North-Eastern Europe in the Stone Age – bridging the gap between the East and the West”The arrival of Corded Ware is without a doubt the clearest example of migration recognized in Finnish Stone Age archaeology. Its appearance has been understood to result from the movement of a new population from the southern or southeastern Baltic Sea area to the southern and western coasts of Finland (Europaeus 1922: 137; Luho 1948: 57; Edgren 1970: 62; Matiskainen 1994: 14) (Fig. 36).