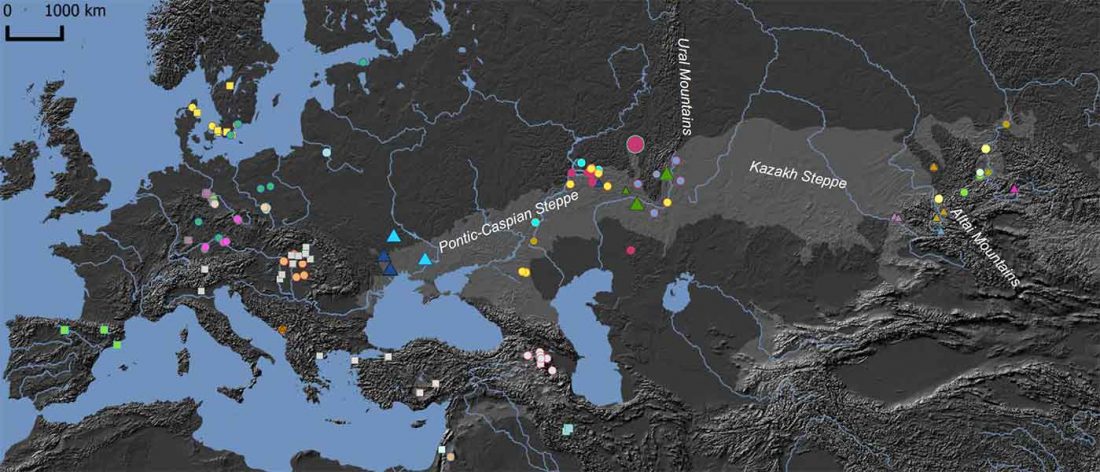
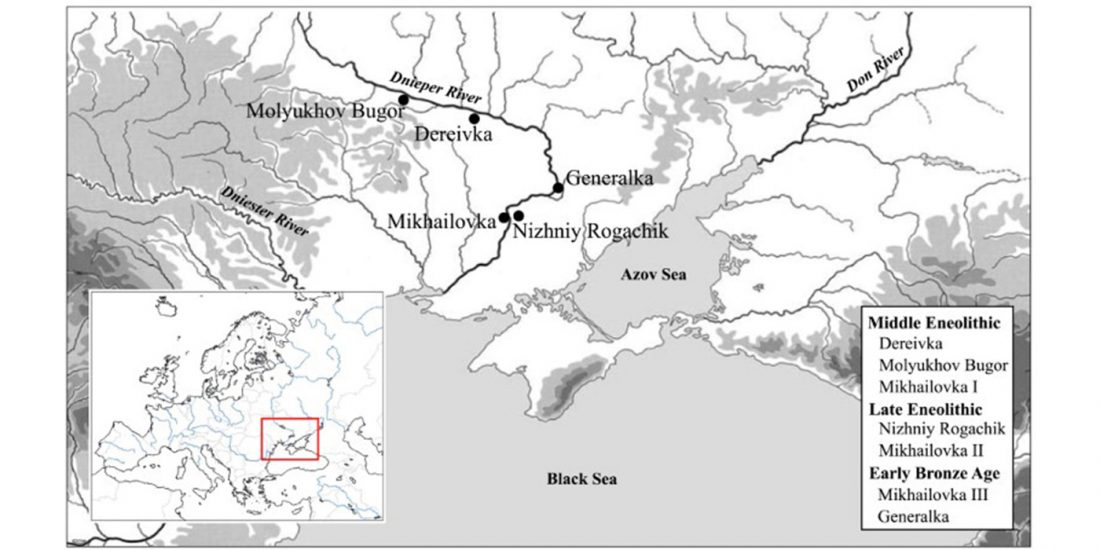
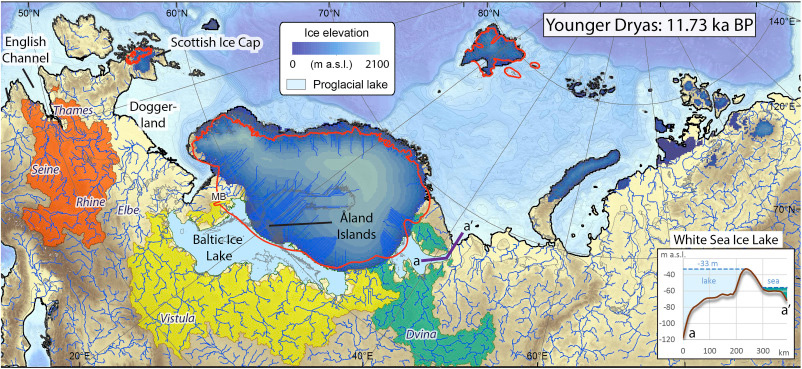
This post is a continuation of a draft on palaeolinguistics and the Proto-Uralic homeland. Or, rather, a preliminary approach to the most likely key to understand the ultimate origin of Proto-Uralic.
Despite the multiple far-fetched proposals of long-range connections between Asian languages and Uralic – e.g. Ural-Altaic, Uralo-Siberian, Eskimo-Uralic, or Uralo-Dravidian – its closest language family is evidently Indo-European, whether by inheritance or by long-lasting intertwined language developments. This supports that Pre-Proto-Uralic and Proto-Uralic developed in Eastern Europe, always close to the Proto-Indo-European homeland. Therefore, it can be assumed that they were subject … Read the rest “Proto-Uralic Homeland (IX): West Caucasian”