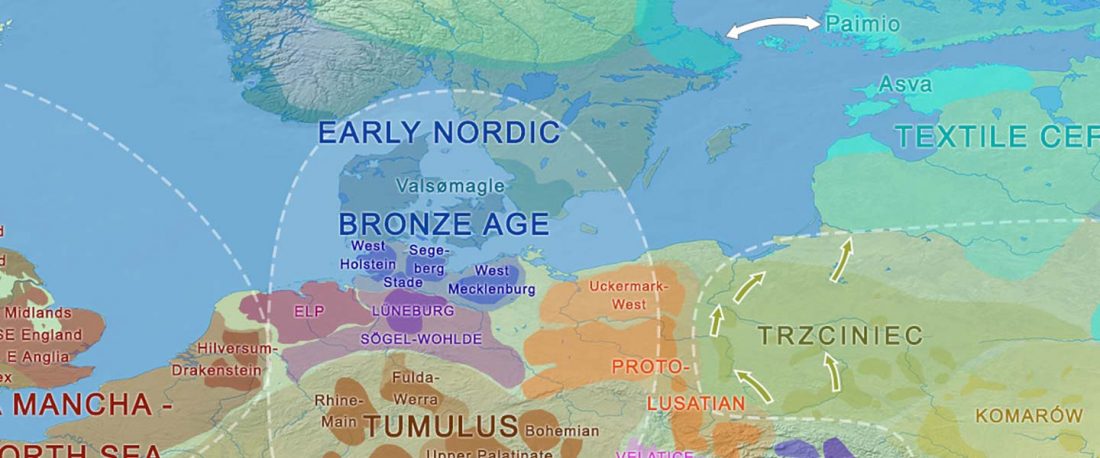
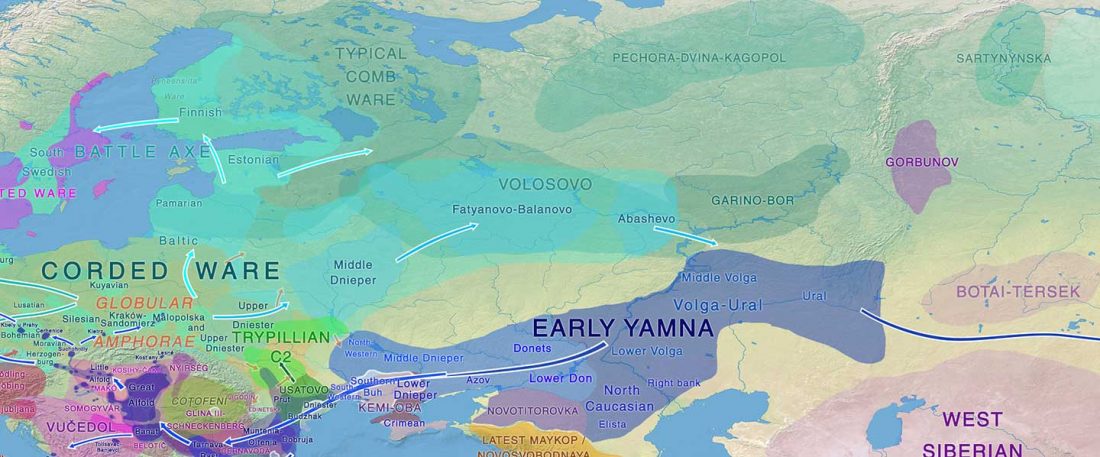
The study of hydrotoponymy shows a prevalent initial Old European layer in central and northern Germany, too, similar to the case in Iberia, France, Italy, and the British Isles.
The recent paper on Late Proto-Indo-European migrations by Frederik Kortlandt relies precisely on this ancestral layer as described by Jürgen Udolph to support a Danubian expansion of North-West Indo-European with East Bell Beakers, identified as the Alteuropäische (Old European) layer that was succeeded by Germanic in the North European Plain.
The Proto-Germanic homeland
The following are excerpts are translated from the German original (emphasis mine) in Udolph’s Namenkundliche Studien … Read the rest “European hydrotoponymy (III): from Old European to Palaeo-Germanic and the Nordwestblock”