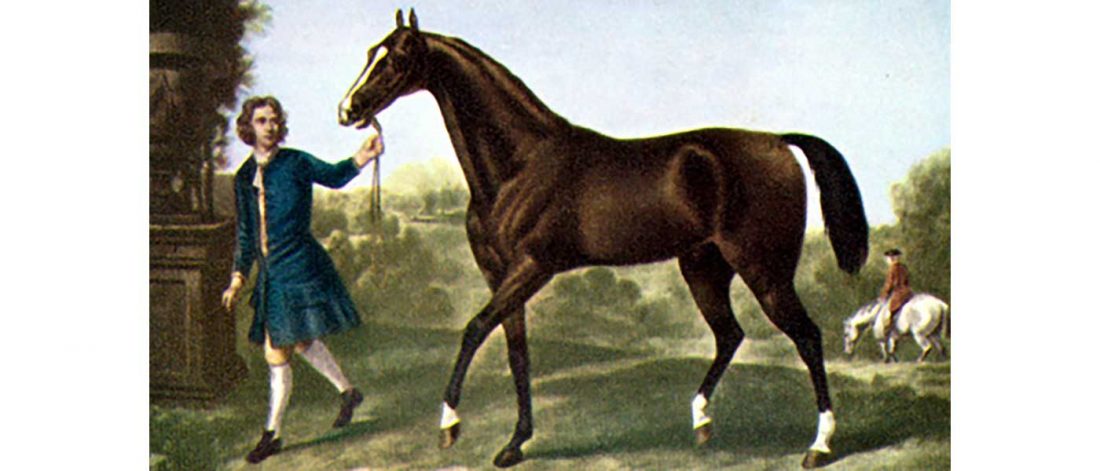
Open access Origin and spread of Thoroughbred racehorses inferred from complete mitochondrial genome sequences: Phylogenomic and Bayesian coalescent perspectives, by Yoon et al. PLOS One (2018).
Abstract (emphasis mine)
… Read the rest “Mitogenomes suggest rapid expansion of domesticated horse before 3500 BC”The Thoroughbred horse breed was developed primarily for racing, and has a significant contribution to the qualitative improvement of many other horse breeds. Despite the importance of Thoroughbred racehorses in historical, cultural, and economical viewpoints, there was no temporal and spatial dynamics of them using the mitogenome sequences. To explore this topic, the complete mitochondrial genome sequences of 14 Thoroughbreds and two Przewalski’s horses were determined. These sequences were analyzed