Open access Complex history of dog (Canis familiaris) origins and translocations in the Pacific revealed by ancient mitogenomes, by Creig et al., Scientific Reports (2018).
Abstract:
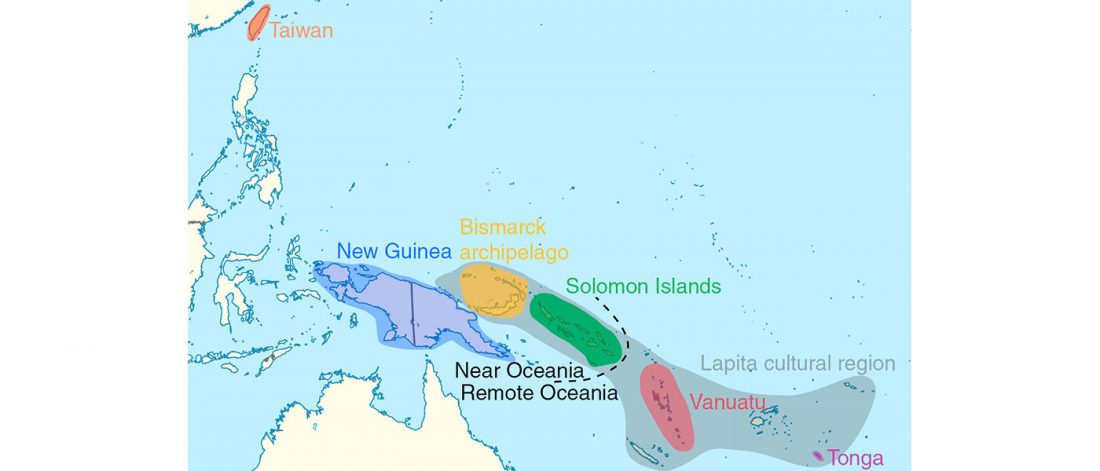
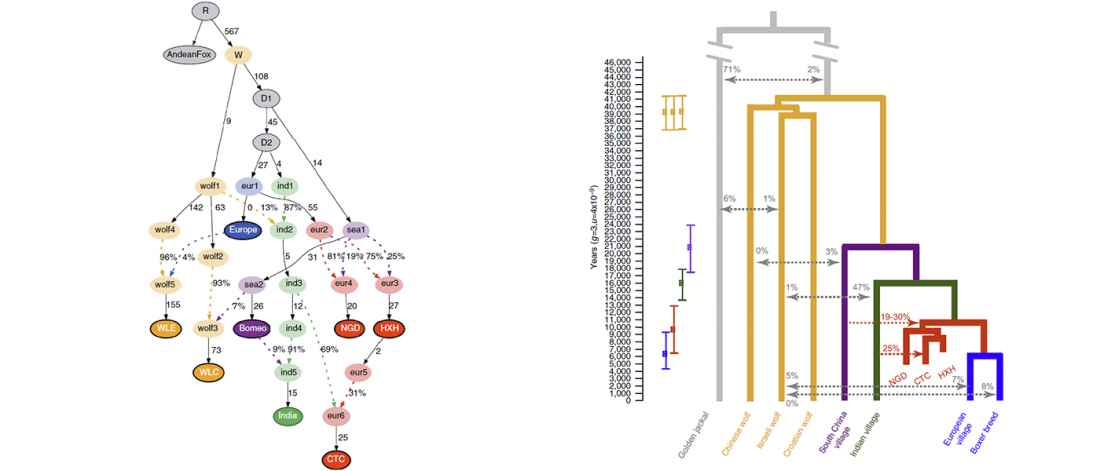
… Read the rest “Complex history of dog origins and translocations in the Pacific revealed by ancient mitogenomes”Archaeological evidence suggests that dogs were introduced to the islands of Oceania via Island Southeast Asia around 3,300 years ago, and reached the eastern islands of Polynesia by the fourteenth century AD. This dispersal is intimately tied to human expansion, but the involvement of dogs in Pacific migrations is not well understood. Our analyses of seven new complete ancient mitogenomes and five partial mtDNA sequences from archaeological dog specimens from Mainland and Island