PhD Thesis Palaeogenomic and biostatistical analysis of ancient DNA data from Mesolithic and Neolithic skeletal remains, by Zuzana Hofmanova (2017) at the University of Mainz.
Abstract:
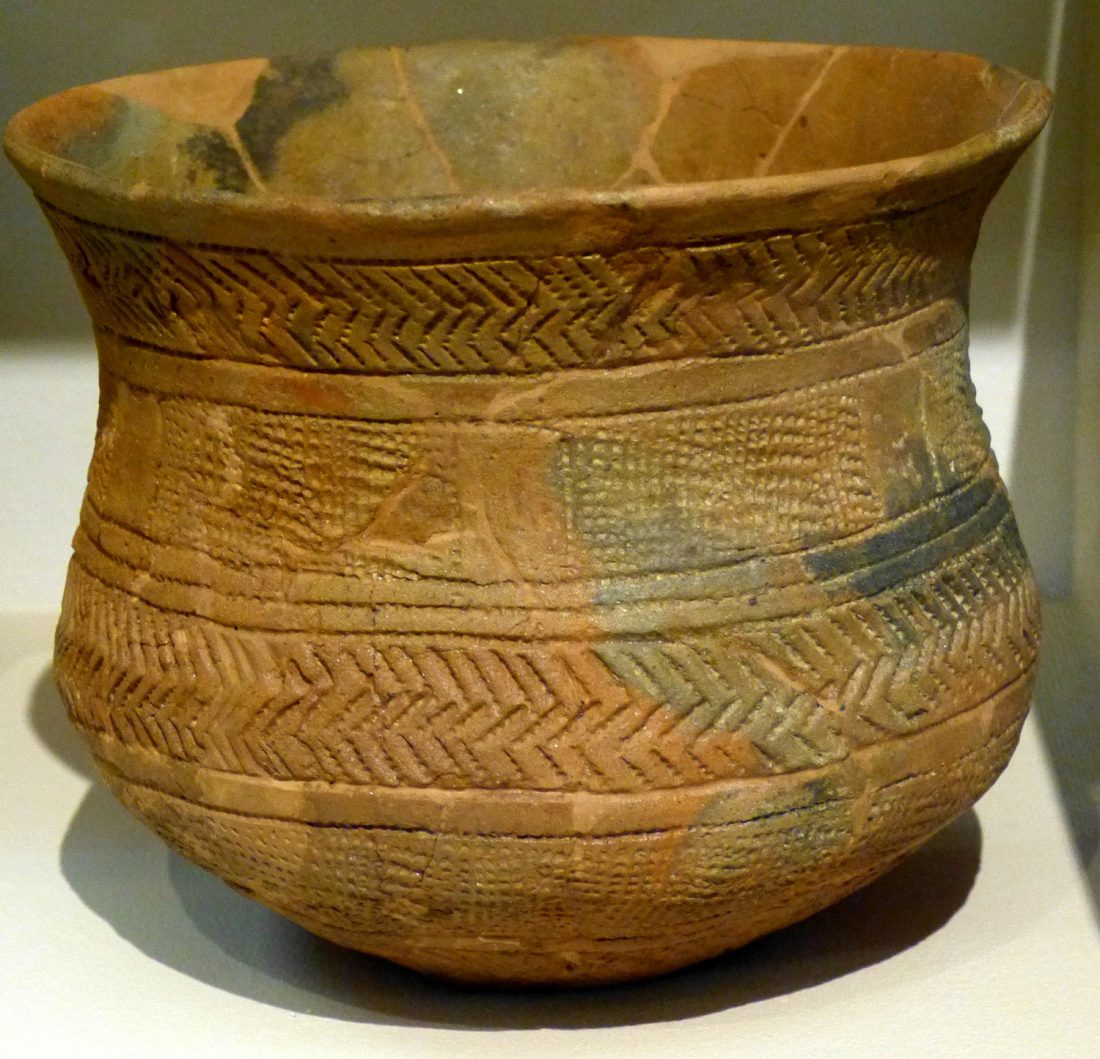
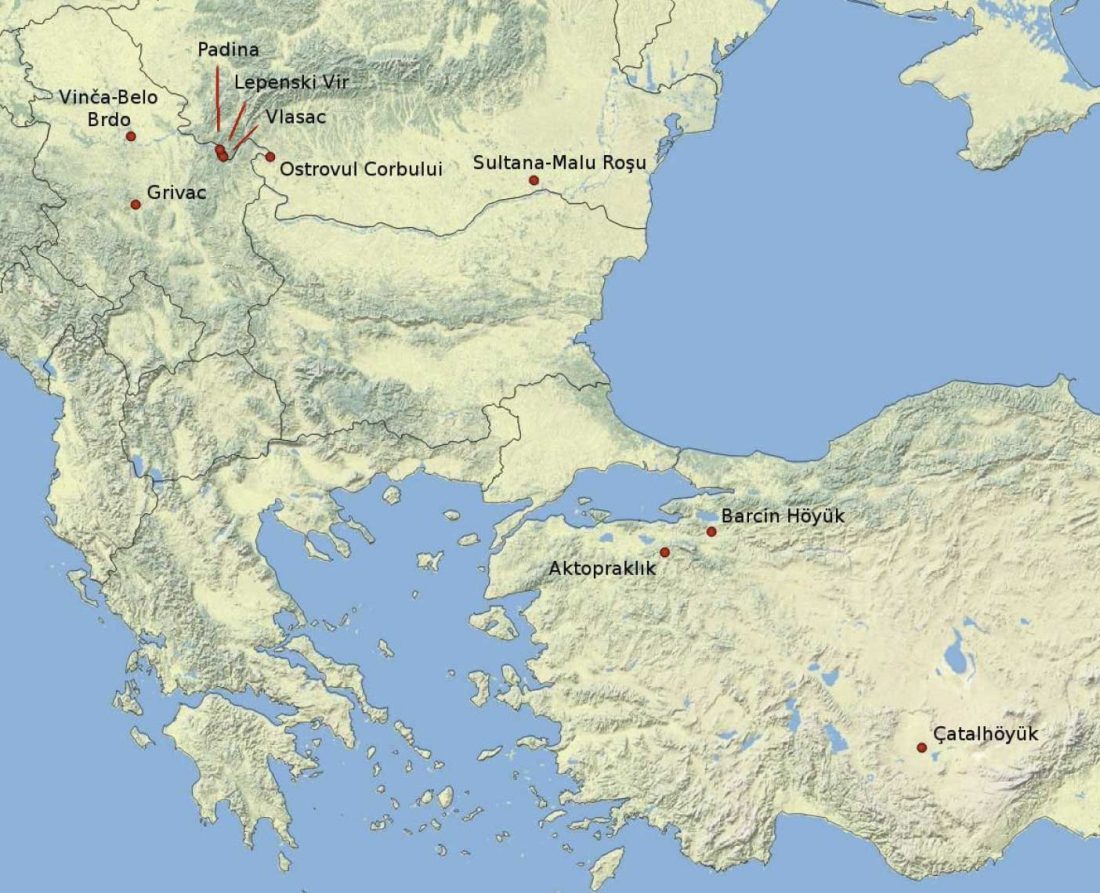
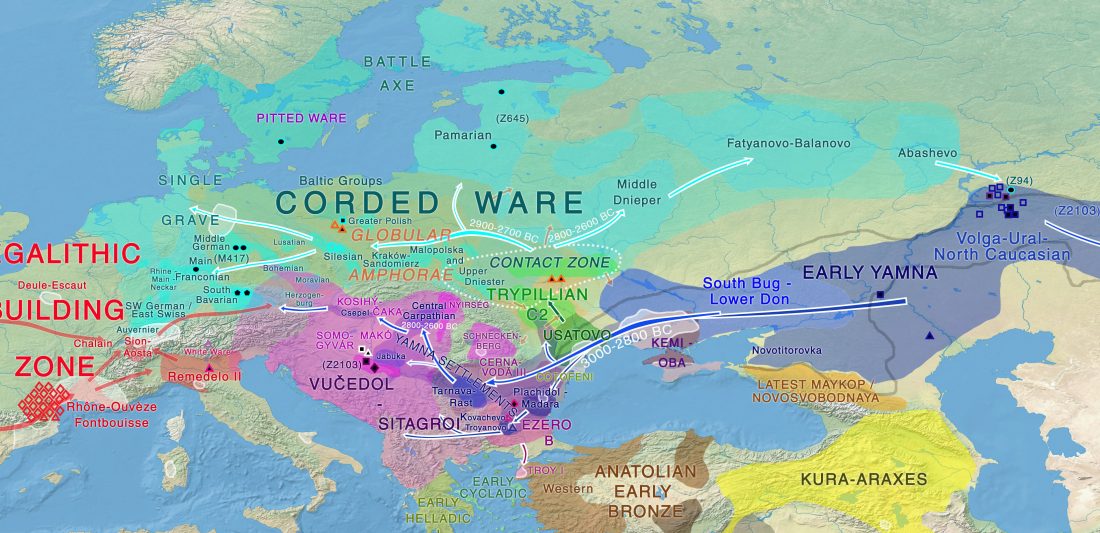
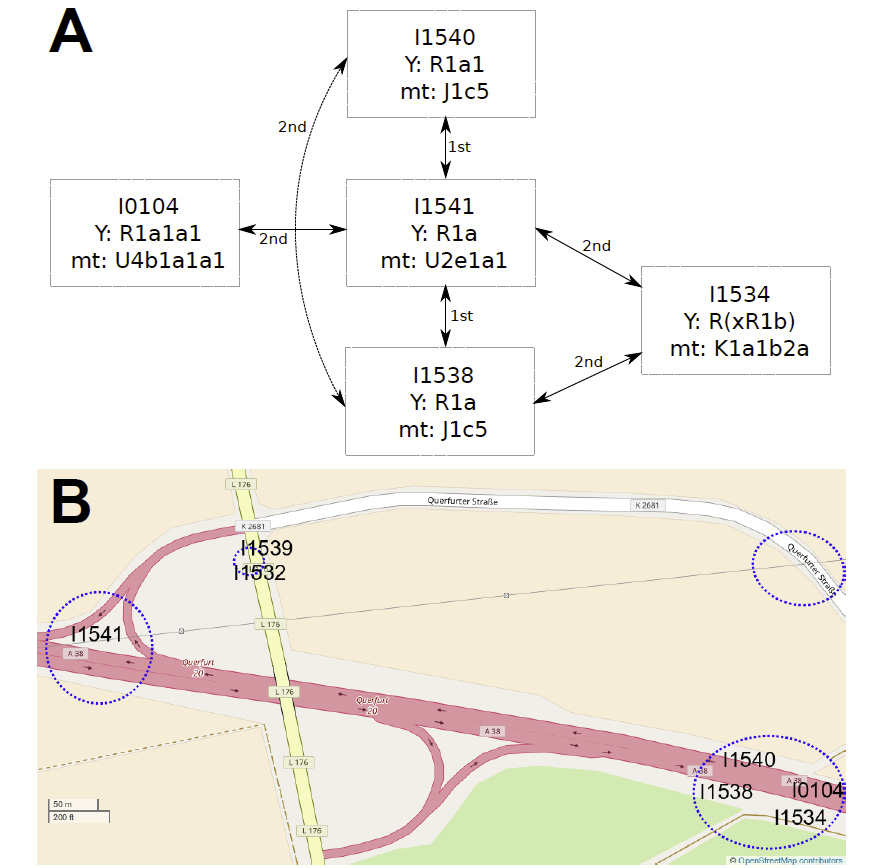
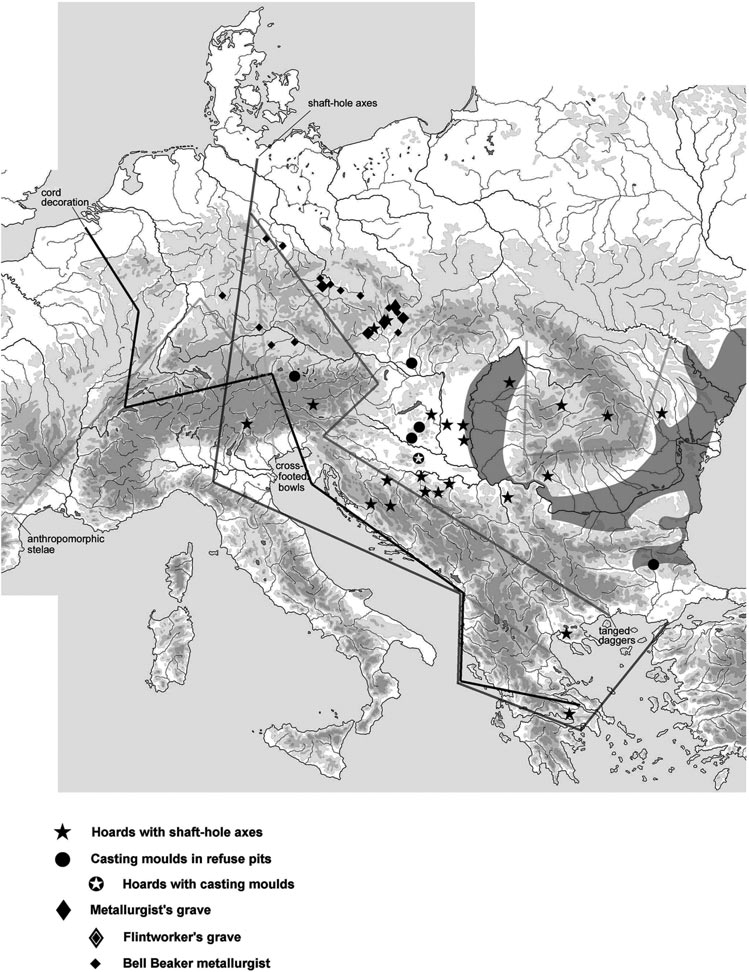
… Read the rest “Palaeogenomic and biostatistical analysis of ancient DNA data from Mesolithic and Neolithic skeletal remains”Palaeogenomic data have illuminated several important periods of human past with surprising im- plications for our understanding of human evolution. One of the major changes in human prehistory was Neolithisation, the introduction of the farming lifestyle to human societies. Farming originated in the Fertile Crescent approximately 10,000 years BC and in Europe it was associated with a major population turnover. Ancient DNA from Anatolia, the presumed source area of the demic spread to