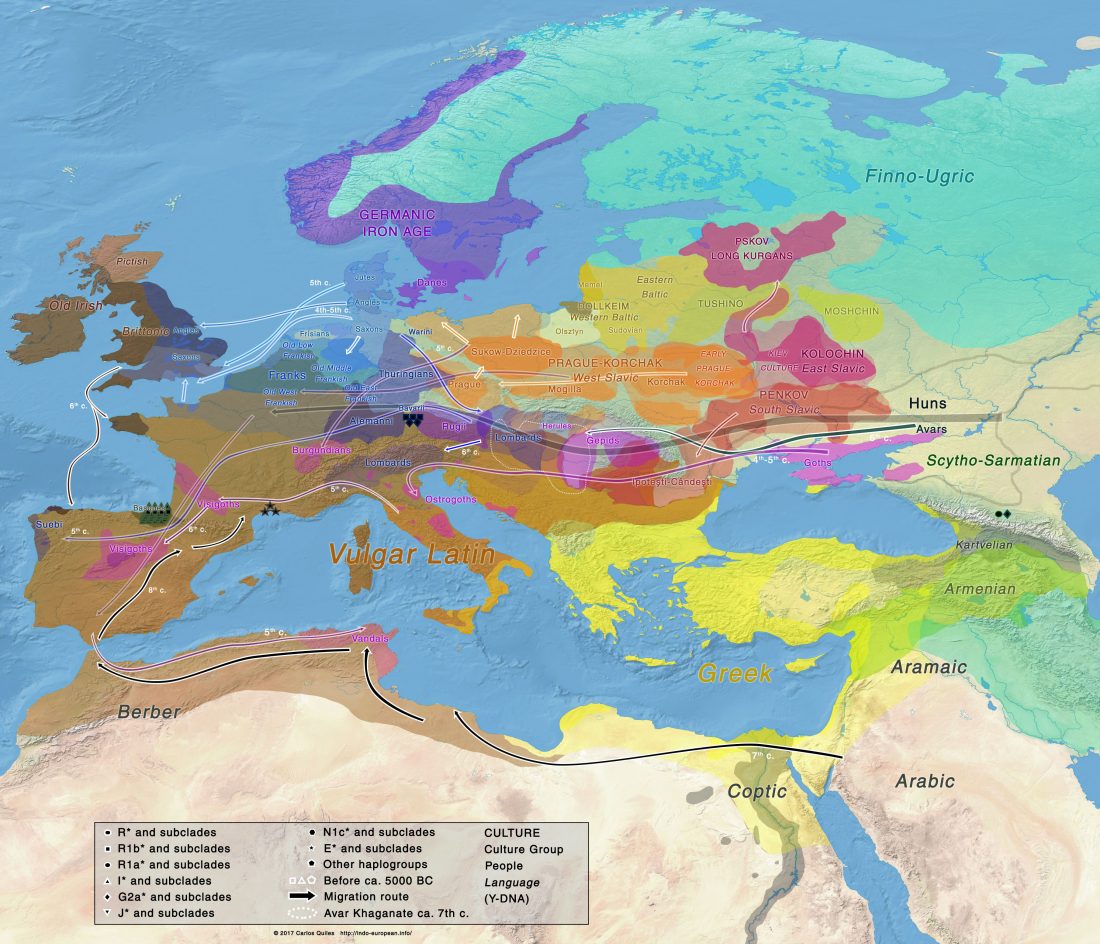
New paper (behind paywall) Family graves? The genetics of collective burials in early medieval southern Germany on trial, by Rott. Päffgen, Haas-Gebhard, Peters, & Harbecka, J Arch Sci (2018) 92: 103–115.
Abstract:
… Read the rest “Mixed haplogroups R1a, R1b, I, in collective burials of early Medieval Bavarians”Simultaneous collective burials appear quite regularly in early medieval linear cemeteries. Despite their relatively regular occurrence, they are seen as extraordinary as the interred individuals’ right to be buried in a single grave was ignored for certain reasons. Here, we present a study examining the possible familial relationship of early medieval individuals buried in this way by using aDNA analysis of mitochondrial HVR-I, Y-STRs, and autosomal miniSTRs.