Open Access Annals of Human Biology (2018), Volume 45, Issue 1, with the title Human population genetics of the Mediterranean.
Among the most interesting articles (emphasis mine):
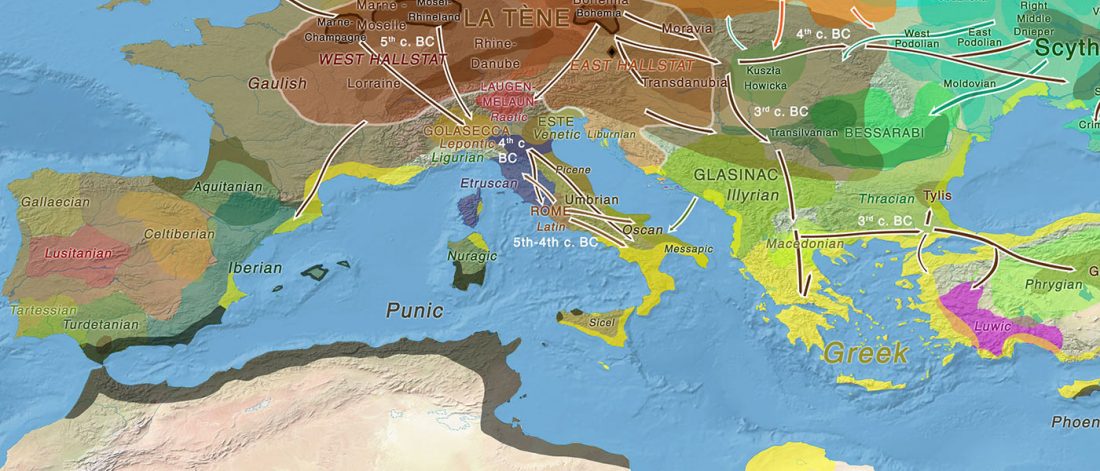
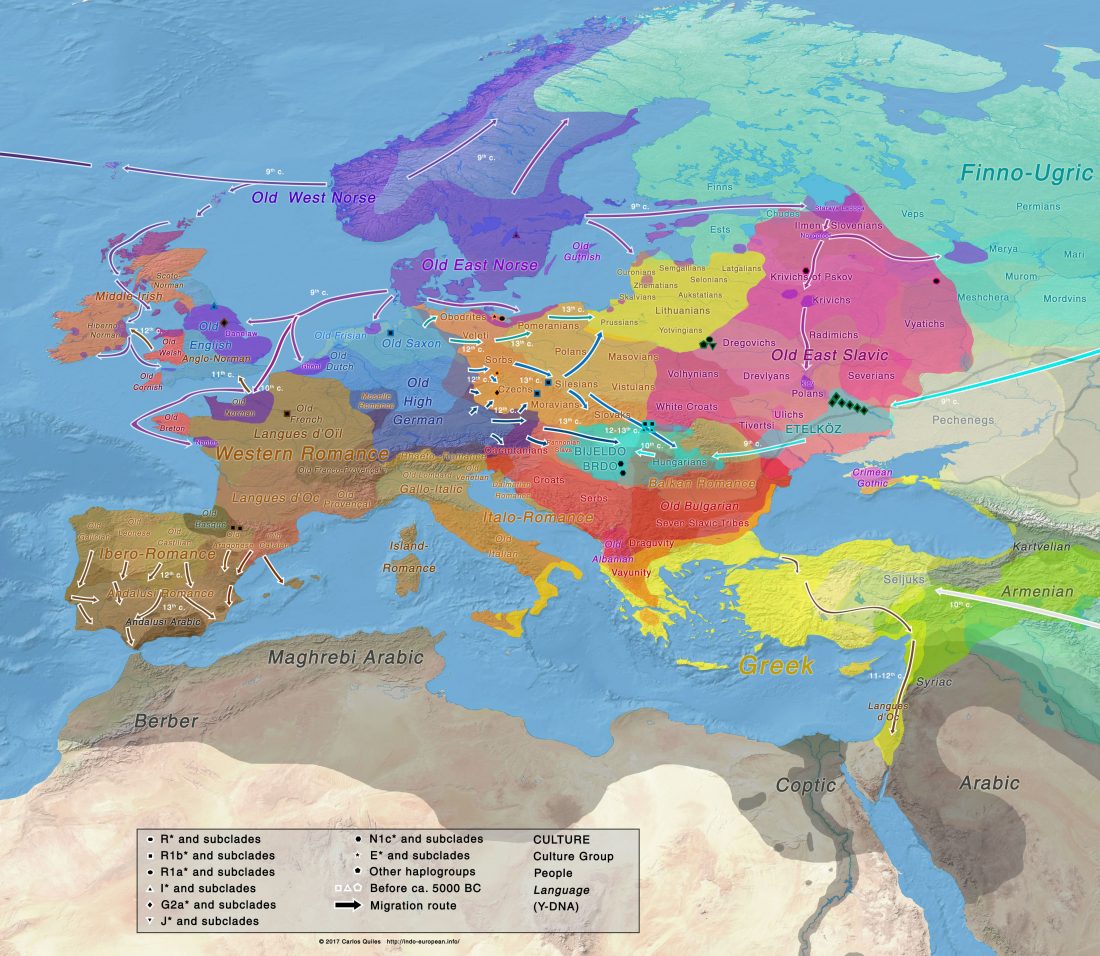
Iron Age Italic population genetics: the Piceni from Novilara (8th–7th century BC), by Serventi, Panicucci, Bodega, et al.
… Read the rest “Y-DNA relevant in the postgenomic era, mtDNA study of Iron Age Italic population, and reconstructing the genetic history of Italians”Background: Archaeological data provide evidence that Italy, during the Iron Age, witnessed the appearance of the first communities with well defined cultural identities. To date, only a few studies report genetic data about these populations and, in particular, the Piceni have never been analysed.
Aims: To provide new data about mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)