Open Access Mitochondrial genomes reveal an east to west cline of steppe ancestry in Corded Ware populations, by Juras et al., Scientific Reports (2018) 8:11603.
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine, references have been deleted for clarity):
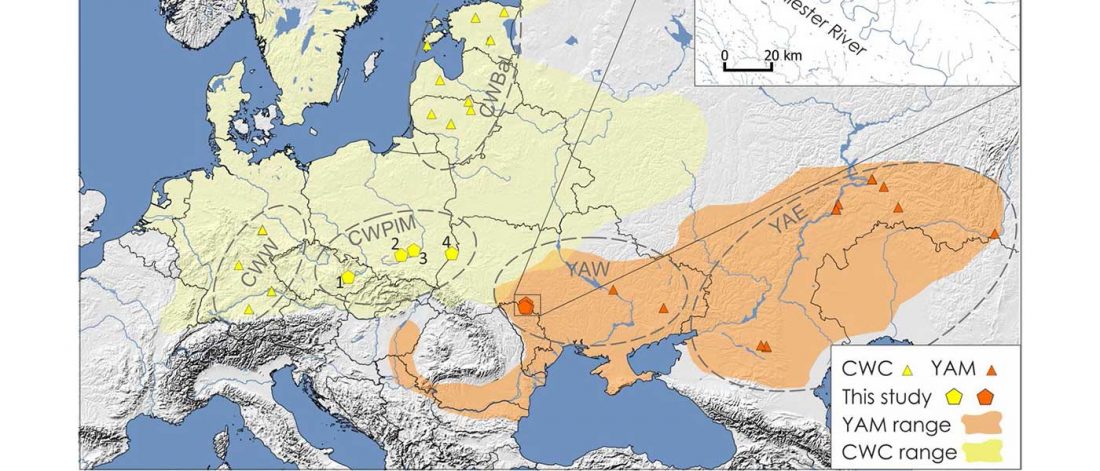
… Read the rest “Mitogenomes show likely origin of elevated steppe ancestry in neighbouring Corded Ware groups”Ancient DNA was extracted from the Corded Ware culture individuals excavated in southeastern Poland (N = 12) and Moravia (N = 3). Late Eneolithic (N = 5) and Bronze Age human remains (N = 25) originated from western Ukraine and came from the Yampil barrow cemetery complex located in the north–western region of the Black Sea. Bronze Age individuals were associated with different archaeological