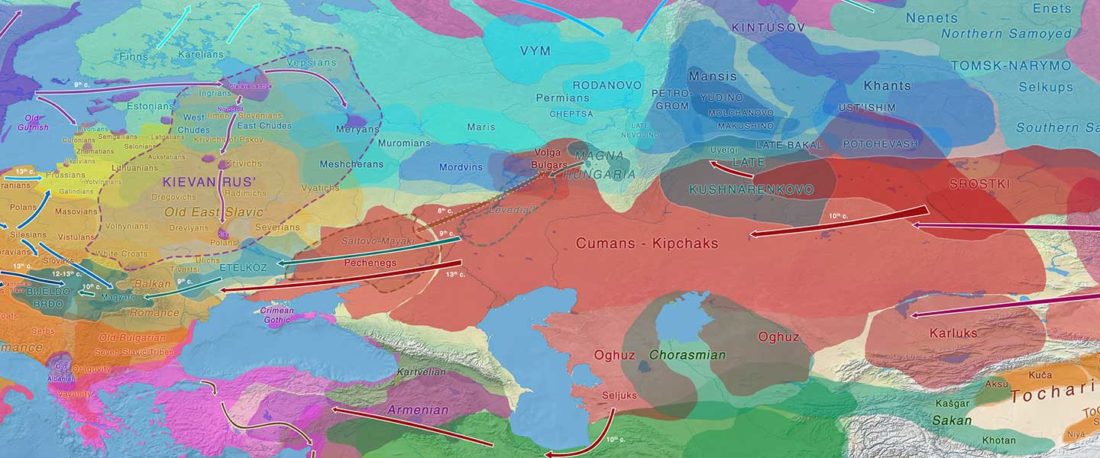
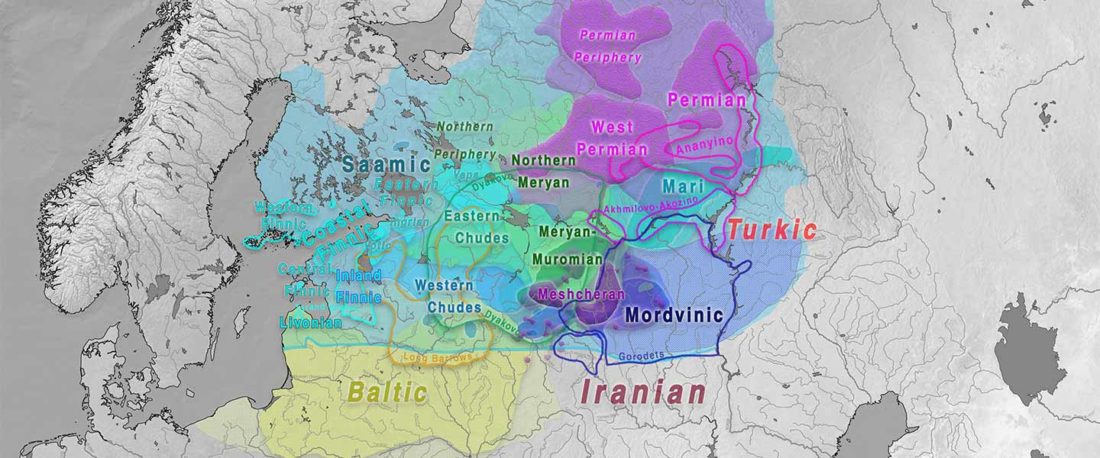
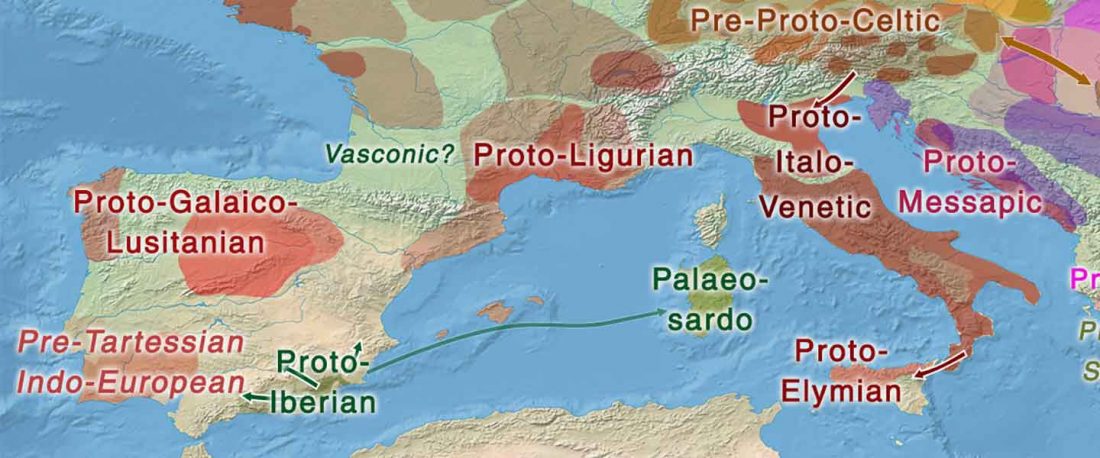
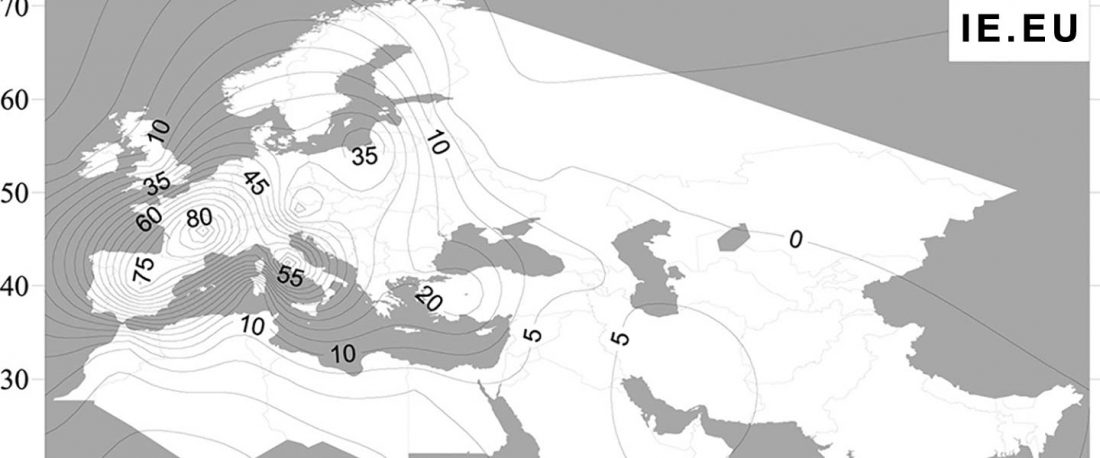
The study of eastern Uralic branches is clearly underdeveloped relative to western ones, and in desperate need of a proper reassessment. This linguistic obscurity contrasts heavily with the decades-long tradition of categorically pinning ethnolinguistic labels (“Ugric” or “Hungarian”) to different prehistorical cultures by (post-)Soviet archaeology, and with the identification of Hungarian as Turkic continuing Turanist trends; 20th century papers showing one of both trends rarely if ever withstand basic scientific scrutiny.
The following is a combination of rewritten excerpts about Ugric in general and Hungarian in particular, as well as some other texts on the linguistic predecessor of the Old … Read the rest “Proto-Hungarian Homeland: East and West of the Urals?”