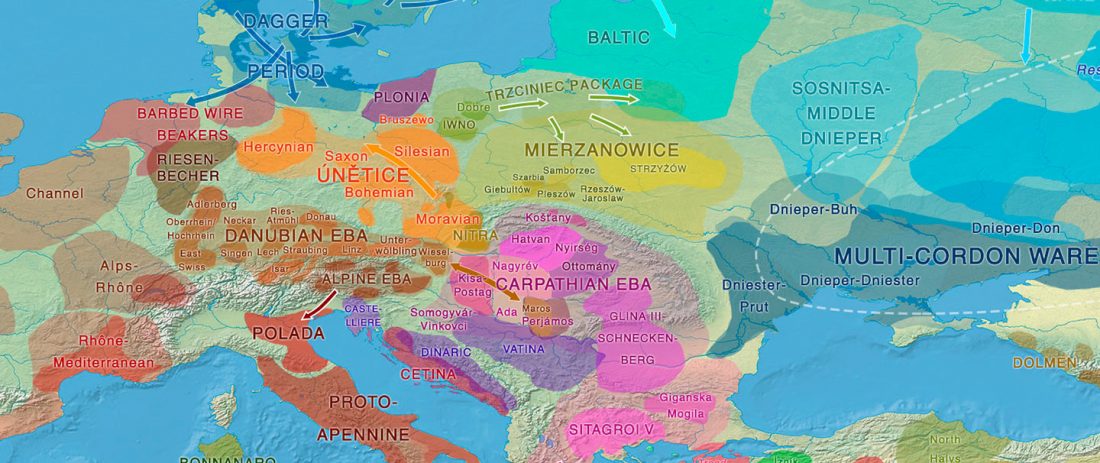
New preprint Kinship, acquired and inherited status, and population structure at the Early Bronze Age Mokrin necropolis in northern Serbia, by Zegarac et al. bioRxiv (2020).
Intersesting excerpts about this 2100-1800 BC cemetery (emphasis mine):
Ancestry
The individual Mokrin genomes are best modelled as a mixture of Central European hunter-gatherers, Aegean Neolithic farmers and influences from the Eastern European steppes (mean qpAdm tail probability individually 0.46, pooled 0.08).
… Read the rest “Maros shows Yamnaya-derived East BBC ancestry and local admixture”We observed no significant variation in the eastern European steppe-like component between individuals. Pooling individuals, admixture proportions are estimated to be around 8% (± 1.2% SE) western hunter gatherers, 55% (±