This post is part of a draft on palaeolinguistics and the Proto-Uralic homeland. See below for the color code of protoforms.
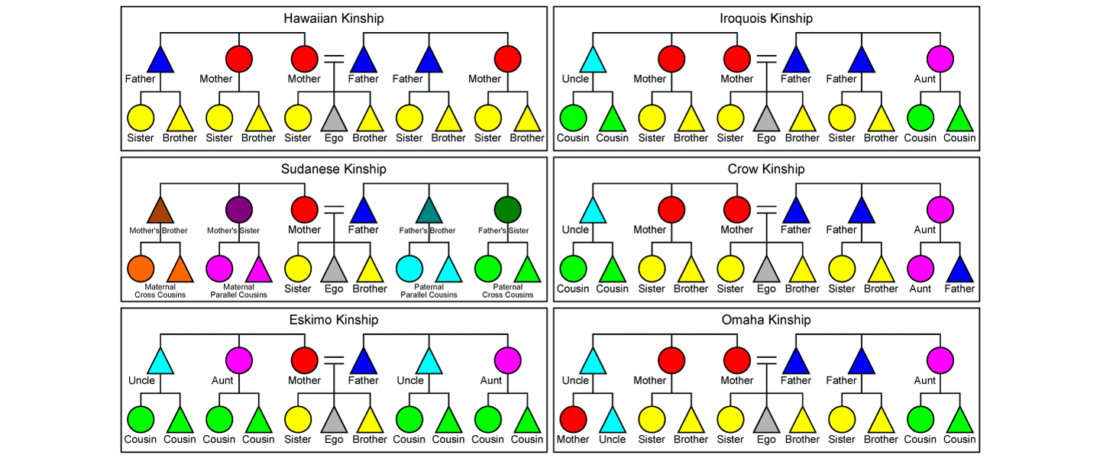
12. Kinship Terminology
12.1. Immediate Family
PU? (Saa.?, Fi.?, Md.?, Ma.?, Kh.?, Ms.?, Hu.?, Smy.?) *äććä?/*eć(ć)ä/*ić(ć)ä/*äjćä ‘father’ (UEW Nº 35). PSmy. was was borrowed into Yukaghir ečē ‘father’. Samoyedic form borrowed into Yukaghir ečē ‘father’ (Aikio 2014: 57)
NOTE. Pre-PSmy. *äjćä? could reflect an earlier Pre-PIIr. *eićo- or PIIr. *aića- ‘to control, to own’. An underlying Pre-PFi., Pre-PSaa. (based on PSaa. *e̮ćē from Skolt and Kildin Saami) and PMa. *ićä could reflect PIIr. … Read the rest “Proto-Uralic Homeland (VII): Kinship & Numerals”