Open access FADS1 and the timing of human adaptation to agriculture, by Sara Mathieson & Iain Mathieson, bioRxiv (2018).
Abstract:
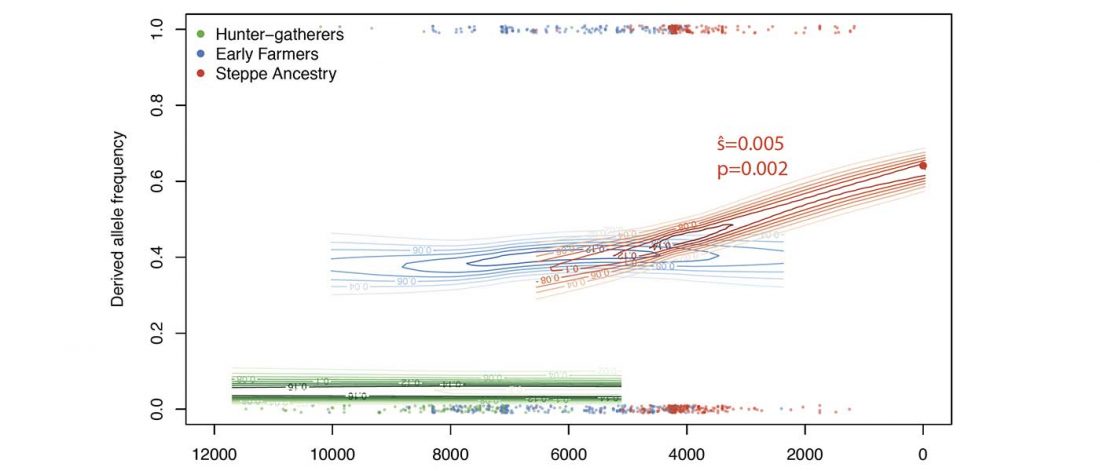
… Read the rest “FADS1 and the timing of human adaptation to agriculture”Variation at the FADS1/FADS2 gene cluster is functionally associated with differences in lipid metabolism and is often hypothesized to reflect adaptation to an agricultural diet. Here, we test the evidence for this relationship using both modern and ancient DNA data. We document pre-out-of-Africa selection for both the derived and ancestral FADS1 alleles and show that almost all the inhabitants of Europe carried the ancestral allele until the derived allele was introduced approximately 8,500 years ago by Early Neolithic farming