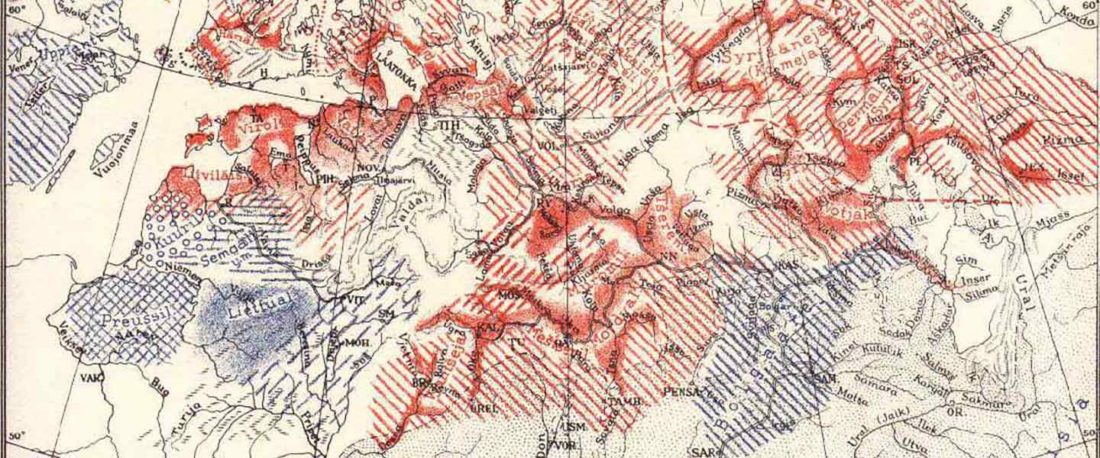
It is firmly established since (at least) the 1980s that Balto-Slavic, Baltic and Slavic show a strong Uralic substrate, even though many details are still the subject of ongoing controversies. Here is how the Baltic linguistic area was described in Thomason’s Language Contact (2001):
… Read the rest “Tug of war between Balto-Slavic and West Uralic (II)”Overall, the Baltic area has the same characteristics as the Balkan area: areal linguistic features are distributed differentially among the languages, and the features themselves vary in details of their structure. As for the sources of the Baltic features, some can be traced to Uralic and some to Indo-European, especially Germanic. The Indo-European languages most