Open access Early Alpine human occupation backdates westward human migration in Late Glacial Europe, by Bortolini et al. bioRxiv (2020).
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
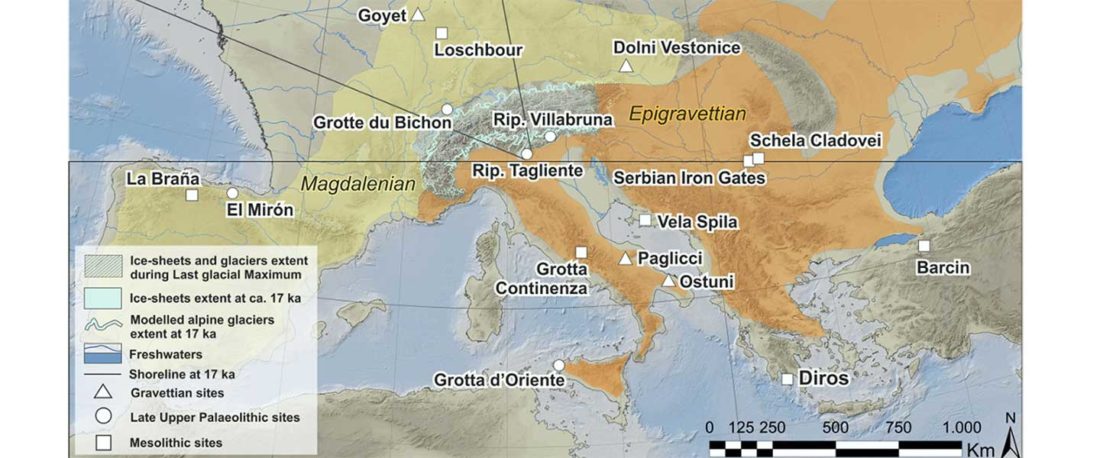
… Read the rest “Epigravettian migrations 3,000 years before Villabruna”To understand the full extent of the role played by demic processes in this key transition in Late Glacial Europe we focused on the left hemimandible of an individual found at Riparo Tagliente (Tagliente2) associated with Late Epigravettian evidence. During the LGM and the Late Glacial, the Adriatic Sea basin played a critical role in shaping the economy and mobility of Epigravettian groups. Geomorphological and sedimentological processes linked to the extension of Alpine glaciers and