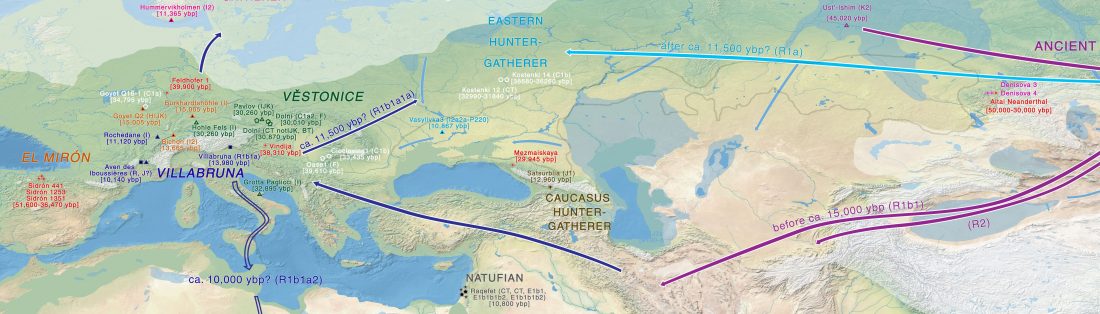
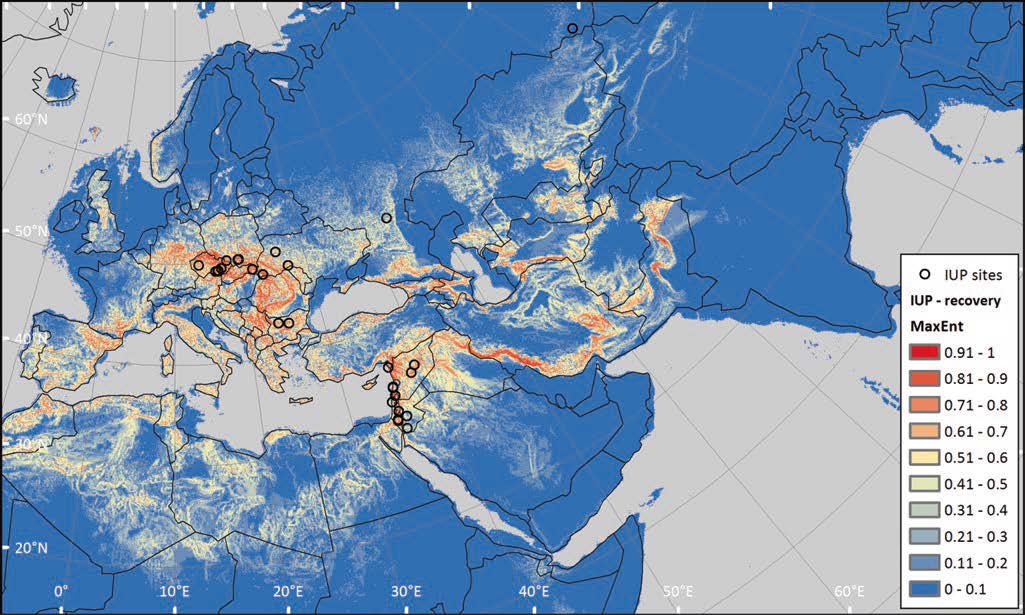
Neanderthal language revisited: not only us, by Dediu and Levinson, Curr Opin Behav Sci (2018) 21:49–55.
Abstract:
… Read the rest “Neanderthal language revisited: speech old and shared with archaic humans”Here we re-evaluate our 2013 paper on the antiquity of language (Dediu and Levinson, 2013) in the light of a surge of new information on human evolution in the last half million years. Although new genetic data suggest the existence of some cognitive differences between Neanderthals and modern humans — fully expected after hundreds of thousands of years of partially separate evolution, overall our claims that Neanderthals were fully articulate beings and that language evolution was gradual are further substantiated by