Expansion of haplogroup G2a in Anatolia possibly associated with the Mature Aceramic period
Preprint Late Pleistocene human genome suggests a local origin for the first farmers of central Anatolia, by Feldman et al. bioRxiv (2018).
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
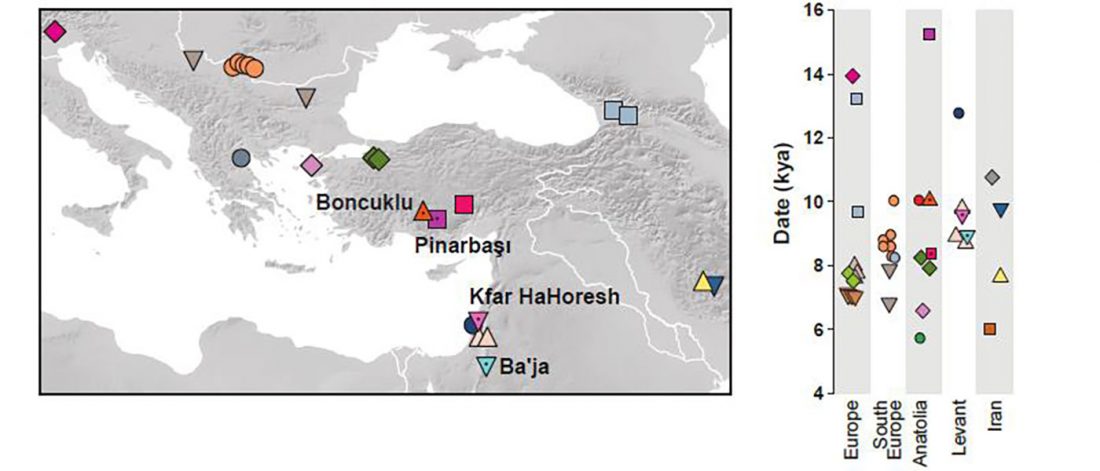
… Read the rest “Expansion of haplogroup G2a in Anatolia possibly associated with the Mature Aceramic period”Anatolian hunter-gatherers experienced climatic changes during the last glaciation and inhabited a region that connects Europe to the Near East. However, interactions between Anatolia and Southeastern Europe in the later Upper Palaeolithic/Epipalaeolithic are so far not well documented archaeologically. Interestingly, a previous genomic study showed that present-day Near-Easterners share more alleles with European hunter-gatherers younger than 14,000 BP (‘Later European HG’) than with earlier ones (‘Earlier European HG’). With ancient genomic data available,